![]() Click to view article in PDF format.
Click to view article in PDF format.
The Bittern Field: Topographic Control of an Eocene Aged ‘‘Channel-Fill’’ Turbidite Reservoir in the U.K. Central North Sea*
By
Dominic McCormick1and Markus Leishman2
Search and Discovery Article #20016 (2004)
*Adapted from “extended abstract” for presentation at the AAPG Annual Meeting, Salt Lake City, Utah, May 11-14, 2003.
1Shell Expro, Aberdeen, United Kingdom, phone: +44 (01224) 883738, ([email protected])
2West Africa Business Unit, Amerada Hess Corporation, 6688 North Central Expressway, Dallas, TX 75206
The Bittern Field is positioned almost 200 km east of Aberdeen and the water depth at the location is 304 ft. The field was discovered in 1996 and lies within block 29/1, which is subdivided into 29/1a (50% Shell/Exxon-Mobil) and 29/1b (50% Amerada Hess and partners, Shell share 14.63%). The field is operated by Shell Expro. The reservoir sandstones at Bittern are lower Eocene Cromarty sands, and the crest of the structure is at 6640 feet TVSS. The deposition of these deep marine turbidite sandstones was a topographically controlled interplay between swelling salt at depth and two older channel sand complexes to the north and south of the Cromarty fairway. In block 29/1, the Cromarty fairway trends west to east; Bittern field is offset towards the northern margin.
|
|
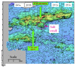
The story of the Tertiary deposition in the Bittern Field area has been constructed by integrating 3D seismic, wireline log (conventional log correlations and formation image data), core, cuttings, and biostratigraphic information. The subdivision of the Cromarty sandstones is based on detailed biostratigraphic (mostly palynology) investigations. A major constraint on the Bittern geological interpretation is the presence of a gas chimney between 3000 and 5500feet TVSS in the claystones overlying the reservoir. The gas chimney extends over most of the Bittern field area, but a geological model has been constructed based on seismically defined lobes (Figure1). Halokinesis beneath the Chalk Group near the center of block 29/1 during Paleocene times is interpreted to have divided an easterly flowing Forties-Andrew system into two; a northern and a southern branch.
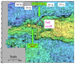
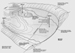
The Andrew sandstones have acted initially as erosive events, downcutting as deep as the top of the Chalk Group (Figure 2). There was subsequently a more extensive Middle Andrew sand depositional event. This now provides an excellent seismic reflector, as it reworked chalk material that has been diagenetically altered such that the ‘‘Middle Andrew’’ sandstones are pervasively cemented and have little in the way of reservoir character. During later Paleocene, the main Forties deposition was farther northeast in the Central North Sea, but subsidiary Forties systems continued to use the older Andrew channels and, by end Paleocene, had mostly back-filled these earlier channel systems. Forties deposition within the Bittern Field area is interpreted as mostly overbank and crevasse-splay type deposits. The Forties-Andrew channel systems were positive topographic features at end Paleocene time and acted as constraining features into which the earliest Eocene Cromarty deposits were deposited. The end Paleocene event was marked biostratigraphically by a major floral change, and this is a regional event in the Central North Sea, here annotated as the Dark Green Marker. The Andrew-Forties isochore map (Figure 3) shows the positions of the two channel complexes, and the Cromarty isochore (Figure 4) shows the ‘‘infill’’ between these two positive features.
The Cromarty sandstones are subdivided based on thin, biostratigraphically constrained, correlatable claystone beds that are interpreted as debris flows. The three main sands are referred to as Lowermost (Figure 5), Lower (Figure 6) and Upper Cromarty (Figure 7), and the intra-Cromarty claystones are the Ochre Marker (between Lowermost and Lower) and the Orange Marker (between the Lower and the Upper Cromarty). These two claystones are correlatable field-wide events and the Ochre can be correlated to wells 5km southwest and east of the field. The sandstones are fine-grained, subarkosic quartz arenites; they show a high net:gross ratio, average being some 90%. The Upper and Lowermost sands have average porosities of about 34%; the Lower Cromarty sands have average porosities of 32% in the discovery well, there being a slight increase in siderite cement in the Lower compared to the other two sands. The earliest Cromarty sand deposits were within the field area, and they constitute a relatively restricted lobate deposit, referred informally as the Purple Lobe of the Lowermost Cromarty. This event was most likely deposited as a splay from the northern channel complex; it appears to have been limited to the east by a salt-induced high. A second, slightly younger event, the Dark Blue Lobe, was deposited to the south and south east of Bittern Field, having been mostly constrained by the southern Forties-Andrew complex. Both of these events, which constitute the Lowermost Cromarty, are capped by the Ochre Marker, which has been identified in the Bittern Field and also the outfield 29/1b-2 and 28/5a-3 wells. The Ochre Marker appears in core to be a slumped and contorted mix of dark gray, silty claystones interbedded with well cemented very fine sandstones. The Lower Cromarty began with the deposition of the Light Blue Lobe, which by-passed the Bittern Field, except for the extreme northeastern part, and was deposited to the east. This was then overlain by the rest of the Lower Cromarty sands, which were deposited as more extensive deposits, filling in more of the ‘‘channel-form’’ fairway between the northern and southern Forties-Andrew channels. These sands were then capped by a second field-wide debris flow, the Orange Marker. The effects of any salt movement during deposition of the Lower Cromarty appears to be considerably less than that during deposition of Lowermost Cromarty, as the Lower Cromarty sands isochore is more uniform, thinning onto the northern margin. The Upper Cromarty sands were deposited as more sheet-like events, for there is even less evidence in the cores for cross-bedding and/or graded bedding. The isochore of the Upper Cromarty in the Bittern field is uniform, approximately 85feet TV. The final deposit of Cromarty sands was the Red lobe. This event was deposited to the southeast of the field and is constrained by the 29/1b-2 well. From here, an ‘‘uplapping’’ event on the seismic pinches out before the Bittern field is reached. The whole area was then blanketed in Sele claystones, before the regional Balder volcanic event occurred.
Upon a quick inspection of the Cromarty sand isochore map in Block 29/1, it may be concluded that these sands were channelized. However, the interplay between salt movement at depth and the topographically positive Andrew-Forties channel complexes resulted in an east-west trending channel-form topographic low which acted as a receptacle for these Early Eocene deposits. |