![]() Click to view article in PDF format.
Click to view article in PDF format.
Comprehensive Use of  VSP
VSP Technology at Elk Hills
Field, Kern County, California*
Technology at Elk Hills
Field, Kern County, California*
By
R.J. Brewer1 and Don Greenfield2
Search and Discovery Article #40091 (2003)
*The viewer is referred
to two other articles about  VSP
VSP , written by the senior author,
The Look Ahead
, written by the senior author,
The Look Ahead  VSP
VSP Survey: Its Utility and Future, Search and Discovery
Article #40060 (2002) and
Survey: Its Utility and Future, Search and Discovery
Article #40060 (2002) and
 VSP
VSP
 Data
Data in Comparison to the Check Shot Velocity Survey, Search and
Discovery Article #40059 (2002).
in Comparison to the Check Shot Velocity Survey, Search and
Discovery Article #40059 (2002).
1Halliburton Energy Services, Houston, TX ([email protected]).
2Occidental of Elk Hills, Inc.
Introduction
To understand accurately subsurface rock
formation and pay zone seismic travel times and velocities within the historic
Elk Hills oil field in Kern County, San Joaquin Valley, California (Figure 1),
Occidental of Elk Hills, Inc. in 1999 embarked on one of the first coordinated
and comprehensive  VSP
VSP survey
survey  data
data acquisition programs in the country. The
trend-setting effort, uncommon in the United States, has helped produce more
accurate surface seismic time-to-drill depth conversions. This result has been
more accurate drilling prospect maps.
acquisition programs in the country. The
trend-setting effort, uncommon in the United States, has helped produce more
accurate surface seismic time-to-drill depth conversions. This result has been
more accurate drilling prospect maps.  VSP
VSP
 data
data has proven to be an effective
means to lower drilling ambiguities as well as overall drilling costs in the Elk
Hills field. It was concluded that rigorous integration of the all the
has proven to be an effective
means to lower drilling ambiguities as well as overall drilling costs in the Elk
Hills field. It was concluded that rigorous integration of the all the  VSP
VSP
 data
data recorded during the campaign into a entire surface and borehole seismic
recorded during the campaign into a entire surface and borehole seismic  data
data set
significantly improved the accuracy of a complex subsurface structural mapping
process. Knowledge of the challenging stratigraphy of the area has also been
enhanced. The result has been markedly improved success rates for exploration
and development well drilling.
set
significantly improved the accuracy of a complex subsurface structural mapping
process. Knowledge of the challenging stratigraphy of the area has also been
enhanced. The result has been markedly improved success rates for exploration
and development well drilling.
Occidental purchased the Elk Hills field from
the United States government in late 1998. As part of a comprehensive plan to
assist development drilling and to prepare for exploration drilling, Oxy
acquired an 80 square mile seismic survey and completed preliminary mapping
throughout the Elk Hills field. Previous 2D and limited  3D
3D seismic acquisition
had proved problematic at best, yielding poor
seismic acquisition
had proved problematic at best, yielding poor  data
data . Near surface low velocity
air sands and extreme topographic variability (Figure
2) hampered surface
seismic
. Near surface low velocity
air sands and extreme topographic variability (Figure
2) hampered surface
seismic  data
data quality. Careful pre-3D acquisition testing and extensive quality
control yielded a
quality. Careful pre-3D acquisition testing and extensive quality
control yielded a  3D
3D seismic volume that was magnitudes better than any previous
acquisition efforts (Figures 3 and
4).
seismic volume that was magnitudes better than any previous
acquisition efforts (Figures 3 and
4).
It has long been
known that  VSP
VSP
 data
data has the established advantage of being generally higher
frequency and better quality than surface seismic. The
has the established advantage of being generally higher
frequency and better quality than surface seismic. The  VSP
VSP ’s one-way travel path
from energy source to receiver helps prevent dissipation of frequency and
amplitude. Consequently, following the
’s one-way travel path
from energy source to receiver helps prevent dissipation of frequency and
amplitude. Consequently, following the  3D
3D seismic acquisition, a comprehensive
wellbore velocity
seismic acquisition, a comprehensive
wellbore velocity  data
data acquisition program was initiated. Although there were
nearly 5,000 wells within the Elk Hills field, prior to the checkshot/
acquisition program was initiated. Although there were
nearly 5,000 wells within the Elk Hills field, prior to the checkshot/ VSP
VSP acquisition program, there were only 11 checkshots within the Elk Hills Field
and another 6 checkshots surrounding the field (Figure 5). During the 1980's,
one or two VSPs had been acquired. However, no digital
acquisition program, there were only 11 checkshots within the Elk Hills Field
and another 6 checkshots surrounding the field (Figure 5). During the 1980's,
one or two VSPs had been acquired. However, no digital  VSP
VSP records were extant;
and only checkshot
records were extant;
and only checkshot  data
data remained.
remained.
|
|
Click to
view sequence of Figures 5 and 6 for comparison of velocity
Acquisition of The
original acquisition plan called for at least one velocity point for
each square mile. As the benefits of velocity Zero offset
While zero
offset VSPs were the goal, many times vibrators had to be offset in
order to suppress noise attributable to ground roll and "ringing" pipe.
Every effort was made to keep offsets less than 500 feet. However, due
to excessive noise and topographic problems, one Whenever
possible, 50-foot level intervals were acquired with a dual station
downhole geophone tool assembly from TD to near surface. These 50-foot
intervals were chosen after careful modeling indicated that this spacing
would be sufficient to correlate with In-field
At the beginning, postulated expenditures for the aggressive acquisition project were a concern. Monetary concerns were mitigated and cost reductions were made possible by competitive bidding along with an Oxy/contractor agreement that guaranteed an average number of VSPs per month in return for significant cost breaks. This agreement has thus far saved Oxy approximately 40% to 50% over individually contracted VSPs.
A
significant part of the exploration and development methodology employed
by Oxy involves being able to produce accurate time-depth functions at
any X-Y location encompassed by the surface seismic
Utilizing a
cost effective and aggressive velocity acquisition program along with
innovative analysis has enabled interpreters to incorporate all
geophysical and geological Some
practitioners have reportedly recommended that ideally one |

 Figure 2:
Digital terrain model showing extreme topographic variations. Yellow and
red denotes higher elevations and blue lower elevations.
Figure 2:
Digital terrain model showing extreme topographic variations. Yellow and
red denotes higher elevations and blue lower elevations. Figure 3:
Elk Hills Oil Field highlighting the locations of major structural
features, well control, and comparative seismic
Figure 3:
Elk Hills Oil Field highlighting the locations of major structural
features, well control, and comparative seismic 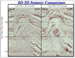 Figure 4:
Comparison of high effort, high quality 2D seismic
Figure 4:
Comparison of high effort, high quality 2D seismic  Figure 5:
Velocity
Figure 5:
Velocity  Figure
6: Velocity
Figure
6: Velocity 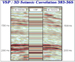 Figure 7:
VSP/3D seismic
Figure 7:
VSP/3D seismic  Figure 8:
Elk Hills south flank location, 351-17G.
Figure 8:
Elk Hills south flank location, 351-17G.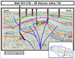 Figure 9:
Seismic backdrop cross section through the 351-17G well.
Figure 9:
Seismic backdrop cross section through the 351-17G well. Figure 10:
Comparison of pre-drill velocity function (KNRVP generated from
substantial checkshot/
Figure 10:
Comparison of pre-drill velocity function (KNRVP generated from
substantial checkshot/