|
Figure Captions
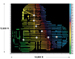 Figure 3.
This source point map shows the location of over 5,000
vibrator points that were used to record over 1,040,000 traces in eight
receiver wells. Color indicates the source point elevations. This 3D/3C VSP recorded near Bakersfield, California in September, 2000 is the
largest 3D VSP ever recorded. Figure 3.
This source point map shows the location of over 5,000
vibrator points that were used to record over 1,040,000 traces in eight
receiver wells. Color indicates the source point elevations. This 3D/3C VSP recorded near Bakersfield, California in September, 2000 is the
largest 3D VSP ever recorded.
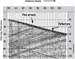 Figure 4.
Raw data recorded with a 4,000 ft long 80 level 3C down hole
receiver array. The data is not filtered or muted and is displayed with
trace-by-trace scaling. The scale across the top is depth in m. Figure 4.
Raw data recorded with a 4,000 ft long 80 level 3C down hole
receiver array. The data is not filtered or muted and is displayed with
trace-by-trace scaling. The scale across the top is depth in m.
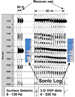 Figure 5.
This is a comparison of the image obtained from surface Figure 5.
This is a comparison of the image obtained from surface
 seismic seismic data and borehole data and borehole  seismic seismic data. The surface data was recorded
simultaneously with the borehole data using the same dynamite shots. The
image on the left is from the surface data. The surface data was recorded
simultaneously with the borehole data using the same dynamite shots. The
image on the left is from the surface  seismic seismic data at the receiver well.
The data has a 40 m CDP spacing. The image on the right was generated
from the borehole data at the receiver well.
The data has a 40 m CDP spacing. The image on the right was generated
from the borehole  seismic seismic data and covers exactly the same time range
and location as the surface data and covers exactly the same time range
and location as the surface  seismic seismic image. The frequency content of the
borehole image. The frequency content of the
borehole  seismic seismic is about twice that of the surface is about twice that of the surface  seismic seismic and the
spatial sampling of the borehole and the
spatial sampling of the borehole  seismic seismic is 5 times greater than
the
surface is 5 times greater than
the
surface  seismic seismic which allows for detailed imaging of lateral changes in
the reservoir properties. which allows for detailed imaging of lateral changes in
the reservoir properties.
Return
to top.
Leaps in Data Acquisition Technology
In the past 18 months a
new type of borehole  seismic seismic receiver array has been introduced that
currently has 80 3-C geophone levels in a single borehole. The design
can be modified to allow as many as 400 to1,000 three-component geophone
levels when fully deployed. receiver array has been introduced that
currently has 80 3-C geophone levels in a single borehole. The design
can be modified to allow as many as 400 to1,000 three-component geophone
levels when fully deployed.
The fundamental
difference between the new and the old borehole arrays is that the new
array is deployed on production tubing wherre the old style of receiver
arrays are deployed using wireline technology. The newly developed
borehole array currently has a geophone spacing of 50 feet, but can be
tailored to any desired spacing. Using a geophone spacing of 50 feet,
the length of the 80-level array is 4,000 feet and the length of a
400-level array is 20,000 feet. Thus, most boreholes can now be filled
from top to bottom with clamped three-component geophones. Geophones can
easily be deployed in horizontal wells because they are conveyed on
standard production tubing using the same method used to deploy electric
submersible pumps.
3-D Borehole  Seismic Seismic Coverage Coverage
The advantage of
deploying a large  number number of borehole of borehole  seismic seismic receivers is that a large
amount of reflection coverage can be obtained per receivers is that a large
amount of reflection coverage can be obtained per  seismic seismic shot, thus
making borehole shot, thus
making borehole  seismic seismic method commercially feasible.
Figure 1 compares the amount of data recorded with a small borehole method commercially feasible.
Figure 1 compares the amount of data recorded with a small borehole
 seismic seismic array as compared to a large 80 level borehole array as compared to a large 80 level borehole  seismic seismic array.
The large increase in reflection coverage per shot that is gained with
large borehole receiver arrays quickly translates to an improved image
quality, because rig time and shot effort are reduced to a minimum and
datasets large enough for a 3-D image can be economically recorded. array.
The large increase in reflection coverage per shot that is gained with
large borehole receiver arrays quickly translates to an improved image
quality, because rig time and shot effort are reduced to a minimum and
datasets large enough for a 3-D image can be economically recorded.
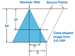
The size and shape of the
 seismic seismic image provided by 3-D VSP data is controlled by the source
locations and path of the borehole. In a vertical well with shots around
the borehole the image is usually cone-shaped and the diameter of the
cone in map view is roughly equal to the depth of the image (Figure
2). By combining data from several wells extensive 3-D images can be
generated. image provided by 3-D VSP data is controlled by the source
locations and path of the borehole. In a vertical well with shots around
the borehole the image is usually cone-shaped and the diameter of the
cone in map view is roughly equal to the depth of the image (Figure
2). By combining data from several wells extensive 3-D images can be
generated.
3-D VSP Examples
Using an 80-level 3-C
array, our company has recorded the four largest 3-D VSPs in the oil and
gas industry. The most recent examples include:
- A 372,000 trace 3-D VSP
survey recorded in four days in West Texas in February 2001.
- A 1,040,000 trace,
eight-well 3-D VSP recorded south of Bakersfield, Calif., in September
2000 (Figure
3).
- A 350,000 trace 3-D VSP in
Alberta, Canada in October 2000.
- A 152,000 trace 3-D VSP
recorded for PanCanadian Petroleum in the Weyburn Field in
Saskatchewan, Canada, in December 1999.
An example shot record
from the Weyburn Survey is shown in
Figure 4. It illustrates the strong, high frequency reflections that
can be recovered in the quiet, downhole environment. In these surveys
much smaller scale reservoir features, including faults and pinch outs,
were mapped with higher resolution than had been possible to map using
surface  seismic seismic methods. methods.
Using the recorded
bandwidth of 10-220 Hz in the Weyburn 3-D VSP survey a resolution of
better than five meters (15 feet) was evident in the final images (Figure
5). In the Edison field survey in California, 150 Hz 3-D VSP data
was recorded in the same area in which surface  seismic seismic data did not
exceed 25 Hz, and the borehole data did not
exceed 25 Hz, and the borehole  seismic seismic image contained much higher
signal to noise ratio features corresponding to a maximum image
frequency well over 100 Hz. image contained much higher
signal to noise ratio features corresponding to a maximum image
frequency well over 100 Hz.
It has been demonstrated
that 3-D VSP data recorded with the 80 level array can be used to image
the entire drainage volume around the well at more than twice the
resolution that can be obtained from a surface  seismic seismic survey. In order
to maximize the use of subsurface 3-D imaging using borehole survey. In order
to maximize the use of subsurface 3-D imaging using borehole  seismic seismic measurements for development and production application, the data can be
processed in the field -- and an initial image delivered within one to
two days. The improved borehole
measurements for development and production application, the data can be
processed in the field -- and an initial image delivered within one to
two days. The improved borehole  seismic seismic instrumentation is now driving
the development of new, innovative and high resolution processing
technologies for borehole instrumentation is now driving
the development of new, innovative and high resolution processing
technologies for borehole  seismic seismic data. data.
Advantages
The principal advantage
of borehole  seismic seismic data is that the frequency content is consistently
much higher than surface data is that the frequency content is consistently
much higher than surface  seismic seismic data recorded over the same location. A
good rule of thumb is that a borehole data recorded over the same location. A
good rule of thumb is that a borehole  seismic seismic image has twice the
frequency content of the surface image has twice the
frequency content of the surface  seismic seismic data. Higher frequency means
higher resolution and less uncertainty in drilling decisions. data. Higher frequency means
higher resolution and less uncertainty in drilling decisions.
The frequency content of
borehole  seismic seismic data is higher than surface data is higher than surface  seismic seismic data because the
wave field only passes through the attenuating near-surface layer one
time rather than twice when both the data because the
wave field only passes through the attenuating near-surface layer one
time rather than twice when both the  sources sources and receivers are at the
surface of the earth. Additionally, the geophones are strongly coupled
to the earth via the geophone clamping mechanism. and receivers are at the
surface of the earth. Additionally, the geophones are strongly coupled
to the earth via the geophone clamping mechanism.
Images from 3-D borehole
surveys are typically generated directly in depth through prestack depth
migration. This allows for an exact tie to depth since the time-depth
relationship is precisely known at the receiver boreholes. Interpreters
can directly tie  seismic seismic data to log properties since logs are always in
depth. A perfect tie to depth minimizes uncertainty in extrapolating
reservoir properties derived from well logs into the data to log properties since logs are always in
depth. A perfect tie to depth minimizes uncertainty in extrapolating
reservoir properties derived from well logs into the  seismic seismic volume. volume.
Conclusions
Borehole  seismic seismic methods
now provide commercially feasible 3-D/3-C high-resolution images for
reservoir characterization. New designs in borehole geophone deployment
equipment allows hundreds of three-component clamped geophones to be
deployed in boreholes instead of the old five and 20 three-component
phones that were deployed using older conventional wire line technology. methods
now provide commercially feasible 3-D/3-C high-resolution images for
reservoir characterization. New designs in borehole geophone deployment
equipment allows hundreds of three-component clamped geophones to be
deployed in boreholes instead of the old five and 20 three-component
phones that were deployed using older conventional wire line technology.
Return
to top.
|
![]() Click to view article in PDF format.
Click to view article in PDF format. seismic
seismic methods have
been used since the beginning of exploration seismology. Check shot surveys were
used to obtain travel times and interval velocities, and 2-D VSPs (Vertical
methods have
been used since the beginning of exploration seismology. Check shot surveys were
used to obtain travel times and interval velocities, and 2-D VSPs (Vertical
 Seismic
Seismic Profiles) and 2-D high-resolution crosswell data also have been
recorded. Until recently however, borehole seismology has be relegated to a
secondary role in seismology because it generated only 1-D or 2-D images -- and
they were obtained at a high cost relative to the amount of information they
provided.
Profiles) and 2-D high-resolution crosswell data also have been
recorded. Until recently however, borehole seismology has be relegated to a
secondary role in seismology because it generated only 1-D or 2-D images -- and
they were obtained at a high cost relative to the amount of information they
provided. seismic
seismic methods was that the fundamental designs of borehole
methods was that the fundamental designs of borehole  seismic
seismic systems
only allowed a small
systems
only allowed a small  number
number of geophones to be deployed in the borehole. Until
about two years ago the maximum
of geophones to be deployed in the borehole. Until
about two years ago the maximum  number
number of three-component (3-C) clamped
geophones that could be deployed in a borehole was around 12. Thus it was
expensive to record enough data to make large surveys economically feasible.
of three-component (3-C) clamped
geophones that could be deployed in a borehole was around 12. Thus it was
expensive to record enough data to make large surveys economically feasible. number
number of geophones in the borehole. The surveys were
expensive and the
of geophones in the borehole. The surveys were
expensive and the  seismic
seismic images were of limited quality because of the small
amount of data recorded per shot.
images were of limited quality because of the small
amount of data recorded per shot.

 Figure
1.
Figure
1. Figure
2.
Figure
2. Figure 3.
Figure 3. Figure 4.
Figure 4. Figure 5.
Figure 5.