|
Summary
Statement
The
seismic  wavelet wavelet is the link between seismic data (traces) on which
interpretations are based and the geology (reflection coefficients) that
is being interpreted, and it must be known to interpret the geology
correctly. However, it is typically unknown, and assumed to be both broad
band and zero is the link between seismic data (traces) on which
interpretations are based and the geology (reflection coefficients) that
is being interpreted, and it must be known to interpret the geology
correctly. However, it is typically unknown, and assumed to be both broad
band and zero  phase phase . Providing this broad band, zero . Providing this broad band, zero  phase phase  wavelet wavelet is the
processing goal of deconvolution. Unfortunately, this goal is rarely met
and the typical is the
processing goal of deconvolution. Unfortunately, this goal is rarely met
and the typical  wavelet wavelet that remains in fully processed seismic data is
mixed- that remains in fully processed seismic data is
mixed- phase phase . Differences in mixed- . Differences in mixed- phase phase wavelets result in mis-ties and
often incorrect interpretations. wavelets result in mis-ties and
often incorrect interpretations.
The
purpose of this article is to show interpreters that significant
improvements in seismic data quality and, correspondingly, their
interpretations of those data are easily obtainable by converting from
mixed- phase phase to zero to zero  phase phase wavelets. wavelets.
Figure
Captions
 Figure
1: Lithologic boundaries define a Reflection Coefficient series, which
when convolved (*) with the field Figure
1: Lithologic boundaries define a Reflection Coefficient series, which
when convolved (*) with the field  wavelet wavelet results in a simulated raw field
trace. Interpreting the highest amplitude event (2.5 seconds) as the
reservoir sand would be wrong. This mixed- results in a simulated raw field
trace. Interpreting the highest amplitude event (2.5 seconds) as the
reservoir sand would be wrong. This mixed- phase phase  wavelet wavelet provides a
distorted image of the actual geology. provides a
distorted image of the actual geology.
 Figure
2: When the field Figure
2: When the field  wavelet wavelet is known, deterministic deconvolution is able to
produce a processed trace that contains the desired broad band zero is known, deterministic deconvolution is able to
produce a processed trace that contains the desired broad band zero
 phase phase  wavelet wavelet . Note, the highest amplitude in the processed trace is now
associated with the largest Reflection Coefficient at the top sand. . Note, the highest amplitude in the processed trace is now
associated with the largest Reflection Coefficient at the top sand.
 Figure
3: Extracted Figure
3: Extracted  wavelet wavelet and the associated amplitude and and the associated amplitude and  phase phase spectrum. spectrum.
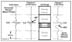 Figure 4: Seismic data containing this mixed-
Figure 4: Seismic data containing this mixed- phase phase  wavelet wavelet will display a
changing peak trough relationship (-90 degrees to +60 degrees) and time
shift (linear will display a
changing peak trough relationship (-90 degrees to +60 degrees) and time
shift (linear  phase phase ) due to the earth’s attenuation of higher
frequencies with depth. For simplicity, the waveforms shown here are only
for the top sand reflector. ) due to the earth’s attenuation of higher
frequencies with depth. For simplicity, the waveforms shown here are only
for the top sand reflector.
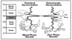
 Figure
5. These wavelets have been extracted from the seismic in Figures 7 and 8 using the well reflection Coefficients Statistical Deconvolution (a)
commonly produces mixed- Figure
5. These wavelets have been extracted from the seismic in Figures 7 and 8 using the well reflection Coefficients Statistical Deconvolution (a)
commonly produces mixed- phase phase wavelets. The broad band - zero wavelets. The broad band - zero  phase phase processing goal of deconvolution has been met using Deterministic
Deconvolution (b).
processing goal of deconvolution has been met using Deterministic
Deconvolution (b).
 Figure
6. The mixed- Figure
6. The mixed- phase phase  wavelet wavelet (Figure 5a) has the character of “Pinocchio
with a beer-gut.” Each reflector has a sharp nose followed by a low-frequency
“beer-gut.” The zero (Figure 5a) has the character of “Pinocchio
with a beer-gut.” Each reflector has a sharp nose followed by a low-frequency
“beer-gut.” The zero
 phase phase  wavelet wavelet (Figure 5b) has all the energy moved up to Pinocchio’s
nose. Reflectors lacking the (Figure 5b) has all the energy moved up to Pinocchio’s
nose. Reflectors lacking the  wavelet wavelet ’s beer-gut more clearly image the
subsurface geology. ’s beer-gut more clearly image the
subsurface geology.
 Figure
7. Seismic data identical to Figure 8 other than the method of
deconvolution, Statistical. This seismic data contains the mixed- Figure
7. Seismic data identical to Figure 8 other than the method of
deconvolution, Statistical. This seismic data contains the mixed- phase phase
 wavelet wavelet of Figure 5a. The “Pinocchio with a “beer-gut” character can
be seen as the trailing low frequencies beneath the high amplitude
reflectors. Mixed- of Figure 5a. The “Pinocchio with a “beer-gut” character can
be seen as the trailing low frequencies beneath the high amplitude
reflectors. Mixed- phase phase wavelets reduces the ability to accurately resolve
the subsurface geology. wavelets reduces the ability to accurately resolve
the subsurface geology.
Click
here for sequence of Figures 7 and 8.
 Figure
8. Seismic data identical to Figure 7 other than method of deconvolution,
Deterministic. This seismic data contains the desired zero Figure
8. Seismic data identical to Figure 7 other than method of deconvolution,
Deterministic. This seismic data contains the desired zero  phase phase  wavelet wavelet (Figure 5b). Note that reflectors are sharper and lack the low-frequency
“beer-gut” of the mixed- (Figure 5b). Note that reflectors are sharper and lack the low-frequency
“beer-gut” of the mixed-  phase phase  wavelet wavelet . In general reflector
continuity, fault breaks, and stratigraphic relationships are
significantly improved. . In general reflector
continuity, fault breaks, and stratigraphic relationships are
significantly improved.
Click
here for sequence of Figures 7 and 8.
 Figure
9. Enlargement of corresponding parts in upper left of Figures 7 and 8,
showing significantly different seismic images from the same subsurface
geology. The zero Figure
9. Enlargement of corresponding parts in upper left of Figures 7 and 8,
showing significantly different seismic images from the same subsurface
geology. The zero  phase phase (b) seismic data not only “looks” better, but
also provides a more accurate image. Mixed- (b) seismic data not only “looks” better, but
also provides a more accurate image. Mixed- phase phase wavelets distort the
seismic image and can lead to incorrect interpretations. wavelets distort the
seismic image and can lead to incorrect interpretations.
 Figure
10. Enlargement from corresponding parts in lower right of Figures 7 and 8
showing significant improvements in the definition of faults are seen on
the zero Figure
10. Enlargement from corresponding parts in lower right of Figures 7 and 8
showing significant improvements in the definition of faults are seen on
the zero  phase phase seismic data (b). “Pinocchio’s beer-gut” in the
mixed- seismic data (b). “Pinocchio’s beer-gut” in the
mixed- phase phase seismic data (a) hangs over the faults, distorting the image.
Reflector continuity and stratigraphic relationships are also improved in
the seismic data containing the zero seismic data (a) hangs over the faults, distorting the image.
Reflector continuity and stratigraphic relationships are also improved in
the seismic data containing the zero  phase phase  wavelet wavelet . .
Return
to top.
Goals
of Deconvolution
Seismic
data can provide a remarkably good image of the subsurface. However,
without knowing the seismic  wavelet wavelet , there are many equally valid surface
geologic interpretations of the actual subsurface geology. The seismic , there are many equally valid surface
geologic interpretations of the actual subsurface geology. The seismic
 wavelet wavelet is the filter through which geology is viewed when interpreting
the image provided by seismic data. is the filter through which geology is viewed when interpreting
the image provided by seismic data.
The
common assumption that seismic data contain a broad band - zero  phase phase
 wavelet wavelet is nearly always wrong. The majority of mis-tie problems between
seismic and synthetics, seismic to seismic of different vintages, and many
of the misinterpretations based on modeling (lithology prediction, trace
attributes, AVO, etc.) are the result of mixed- is nearly always wrong. The majority of mis-tie problems between
seismic and synthetics, seismic to seismic of different vintages, and many
of the misinterpretations based on modeling (lithology prediction, trace
attributes, AVO, etc.) are the result of mixed- phase phase wavelets remaining in
fully processed seismic data. wavelets remaining in
fully processed seismic data.
The
convolutional model is useful for understanding how changes in rock
properties (velocity and density) result in the waveform changes observed
in seismic data. At lithologic boundaries the magnitude of change
(reflection coefficient) in these rock properties determines how much of
the  wavelet wavelet ’s energy is reflected to the surface. In acquiring seismic
data (Figure 1), the subsurface is illuminated with sonic energy (field ’s energy is reflected to the surface. In acquiring seismic
data (Figure 1), the subsurface is illuminated with sonic energy (field
 wavelet wavelet ), which is reflected from these acoustic boundaries and recorded
at the surface as a raw field trace. ), which is reflected from these acoustic boundaries and recorded
at the surface as a raw field trace.
Where
lithologic boundaries are widely separated, the field  wavelet wavelet can be seen
“hanging” below the reflector at 2.2 seconds (Figure
1). When
boundaries are more closely spaced (2.3-2.5 seconds), the can be seen
“hanging” below the reflector at 2.2 seconds (Figure
1). When
boundaries are more closely spaced (2.3-2.5 seconds), the  wavelet wavelet is not
as easily seen due to the wavelets being summed together. This summing is
also known as convolution. is not
as easily seen due to the wavelets being summed together. This summing is
also known as convolution.
The
convolutional model states that all seismic traces are the result of
convolving (summing) the  wavelet wavelet with the reflection coefficient series.
In Figure 1, the raw field trace images the desired geology (lithologic
boundaries = reflection coefficients), but it is through the complex
filter (convolution) of the field with the reflection coefficient series.
In Figure 1, the raw field trace images the desired geology (lithologic
boundaries = reflection coefficients), but it is through the complex
filter (convolution) of the field  wavelet wavelet . .
Exploring
for the sand in Figure 1 and assuming the  wavelet wavelet is broad band - zero is broad band - zero
 phase phase , the sand should be the largest peak. The largest peak, however, is
at 2.5 seconds, due to the field , the sand should be the largest peak. The largest peak, however, is
at 2.5 seconds, due to the field  wavelet wavelet not being zero not being zero  phase phase . When the . When the
 wavelet wavelet in the seismic trace is unknown, the geology is unknown.
Interpretations are not made on raw field traces, but even on processed
seismic traces, the in the seismic trace is unknown, the geology is unknown.
Interpretations are not made on raw field traces, but even on processed
seismic traces, the  wavelet wavelet must be known to more correctly interpret the
geology. must be known to more correctly interpret the
geology.
The
seismic processing procedure designed to convert the field  wavelet wavelet to the
desired broad band - zero to the
desired broad band - zero  phase phase  wavelet wavelet is deconvolution. The two common
methods of deconvolution are deterministic deconvolution and statistical
deconvolution. is deconvolution. The two common
methods of deconvolution are deterministic deconvolution and statistical
deconvolution.
Deterministic
deconvolution can be applied when the field  wavelet wavelet is known (measured
and/or modeled). As shown in Figure 2, when the is known (measured
and/or modeled). As shown in Figure 2, when the  wavelet wavelet is known, an
inverse can be determined and the field trace deconvolved to contain the
desired zero is known, an
inverse can be determined and the field trace deconvolved to contain the
desired zero  phase phase  wavelet wavelet . When processed traces contain a zero . When processed traces contain a zero  phase phase
 wavelet wavelet , increases in rock velocity (shale to sand) will result in peaks
(positive reflection coefficients). , increases in rock velocity (shale to sand) will result in peaks
(positive reflection coefficients).
More
typically, the field  wavelet wavelet is unknown and statistical deconvolutions
must be used. Statistical deconvolutions must make assumptions about both
the is unknown and statistical deconvolutions
must be used. Statistical deconvolutions must make assumptions about both
the  wavelet wavelet and the reflection coefficient series. The most common
assumption is that the and the reflection coefficient series. The most common
assumption is that the  wavelet wavelet is minimum is minimum  phase phase and that the reflection
coefficient series is random. and that the reflection
coefficient series is random.
Return
to top.
Over
90 percent of all seismic data are processed assuming minimum  phase phase .
Examples of a few of the more popular minimum .
Examples of a few of the more popular minimum  phase phase deconvolutions include
Spiking, Gapped, Predictive, and Adaptive. Unfortunately, most field
wavelets are not minimum deconvolutions include
Spiking, Gapped, Predictive, and Adaptive. Unfortunately, most field
wavelets are not minimum  phase phase , and that basic assumption is not met.
Using minimum , and that basic assumption is not met.
Using minimum  phase phase deconvolutions typically results in processed traces
that contain mixed- deconvolutions typically results in processed traces
that contain mixed- phase phase rather than the desired zero rather than the desired zero  phase phase wavelets. wavelets.
A
 wavelet wavelet extracted deterministically from seismic data (using the known
reflection coefficient series from the well) that had been deconvolved
assuming minimum extracted deterministically from seismic data (using the known
reflection coefficient series from the well) that had been deconvolved
assuming minimum  phase phase is shown in Figure 3. Note that this is shown in Figure 3. Note that this  wavelet wavelet is not
zero is not
zero  phase phase ( ( phase phase spectrum: constant zero value for all frequencies) but
is mixed spectrum: constant zero value for all frequencies) but
is mixed  phase phase (non-linear, variable for all frequencies). (non-linear, variable for all frequencies).
In
describing mixed- phase phase wavelets, it is useful to group frequency into
bands in which a linear fit can be extrapolated to the wavelets, it is useful to group frequency into
bands in which a linear fit can be extrapolated to the  phase phase axis ( axis ( phase phase spectrum). For the
spectrum). For the  wavelet wavelet in Figure 3, the higher frequencies (20-65
Hertz) have a in Figure 3, the higher frequencies (20-65
Hertz) have a  phase phase of -90 degrees, while the lower frequencies (5-20
Hertz) have a of -90 degrees, while the lower frequencies (5-20
Hertz) have a  phase phase of +60 degrees. of +60 degrees.
The
description of this mixed- phase phase  wavelet wavelet is interpretive, and could be
described differently by using other frequency bands. Using the bands
shown in Figure 3, with most of the power (amplitude spectrum squared) in
the 20-65 Hertz band, this is interpretive, and could be
described differently by using other frequency bands. Using the bands
shown in Figure 3, with most of the power (amplitude spectrum squared) in
the 20-65 Hertz band, this  wavelet wavelet has the has the  phase phase characteristic of -90
degrees (trough-peak). characteristic of -90
degrees (trough-peak).
An
important ramification of mixed- phase phase wavelets is that their peak-trough
relationships will change with depth due to the effects of earth
filtering. In the case of the wavelets is that their peak-trough
relationships will change with depth due to the effects of earth
filtering. In the case of the  wavelet wavelet shown in Figure
3, shallow in the
section where the earth has not filtered the higher frequences (maximum
power 20-60 Hertz), positive reflectors (low to high velocity) will
display -90 degrees (trough-peak). Deep in the section where the high
frequencies have been attenuated (dashed line in the amplitude spectra, Figure
3), the shown in Figure
3, shallow in the
section where the earth has not filtered the higher frequences (maximum
power 20-60 Hertz), positive reflectors (low to high velocity) will
display -90 degrees (trough-peak). Deep in the section where the high
frequencies have been attenuated (dashed line in the amplitude spectra, Figure
3), the  wavelet wavelet will appear with the will appear with the  phase phase characteristics of the
lower frequencies and will have a characteristics of the
lower frequencies and will have a  phase phase of +60 degrees (peak-trough). of +60 degrees (peak-trough).
Mixed- phase phase wavelets are the most common wavelets found in seismic data and can have a
strong affect on interpretations. This is shown in Figure 4 by filtering
back (5-20 Hertz) the processed
wavelets are the most common wavelets found in seismic data and can have a
strong affect on interpretations. This is shown in Figure 4 by filtering
back (5-20 Hertz) the processed  wavelet wavelet to illustrate strong earth
filtering. The identical reservoir sandstone would appear as a trough-peak
(-90 degrees) shallow (1.0 seconds) in the section and as a peak-trough
(+60 degrees) deeper (3.0 seconds) in the section. This change in the
peak-trough relationship due to earth filtering is commonly observed when
comparing constant to illustrate strong earth
filtering. The identical reservoir sandstone would appear as a trough-peak
(-90 degrees) shallow (1.0 seconds) in the section and as a peak-trough
(+60 degrees) deeper (3.0 seconds) in the section. This change in the
peak-trough relationship due to earth filtering is commonly observed when
comparing constant  phase phase synthetics (from well logs) to seismic data.
Typically this problem is compensated by applying a bulk time shift
(linear synthetics (from well logs) to seismic data.
Typically this problem is compensated by applying a bulk time shift
(linear  phase phase shift) and changing the constant shift) and changing the constant  phase phase  wavelet wavelet used in
making the synthetic. used in
making the synthetic.
Combining
these corrections will approximate the curved shape of the mixed- phase phase (Figure
3) with a single sloping line (time shift) that intersects the (Figure
3) with a single sloping line (time shift) that intersects the
 phase phase axis at the desired constant axis at the desired constant  phase phase . A different time shift and
constant . A different time shift and
constant  phase phase is required to match the curve deeper in the section due to
the earth’s absorption of higher frequencies. is required to match the curve deeper in the section due to
the earth’s absorption of higher frequencies.
Due
to the mixed- phase phase  wavelet wavelet , peak-trough relationship change as a function
of earth absorption (Figure 4), and interpretations based on amplitudes,
AVO, attributes, etc., are likely to be incorrect. The solutions to these
problems are to convert the mixed- , peak-trough relationship change as a function
of earth absorption (Figure 4), and interpretations based on amplitudes,
AVO, attributes, etc., are likely to be incorrect. The solutions to these
problems are to convert the mixed- phase phase  wavelet wavelet to zero to zero  phase phase in seismic
processing or to extract the mixed- in seismic
processing or to extract the mixed- phase phase  wavelet wavelet , know its effects, and
use it when modeling. , know its effects, and
use it when modeling.
When
interpreting seismic data, it is important to realize that the actual
subsurface geology is always being viewed through the filter of the
seismic  wavelet wavelet . Although deconvolution is designed to provide a broad
band - zero . Although deconvolution is designed to provide a broad
band - zero  phase phase  wavelet wavelet , this goal is typically not met, and most
seismic data contain mixed- , this goal is typically not met, and most
seismic data contain mixed- phase phase wavelets. Mixed- wavelets. Mixed- phase phase wavelets affect
interpretations and, as noted below, degrade the quality of seismic data. wavelets affect
interpretations and, as noted below, degrade the quality of seismic data.
Return
to top.
Comparison
of Seismic Data After Different Methods of Deconvolution
The
wavelets shown in Figure 5 were extracted from the seismic data in
Figures
7 and 8. Both sets of seismic data were processed identically, other than
the method of deconvolution (statistical-minimum  phase phase vs. deterministic).
The wavelets were extracted deterministically, by cross-correlating
(Wiener-Levinson filter) seismic traces with the known geology derived
from the subsurface well reflection coefficient series. At first glance,
most interpreters would be content having either of these “spike-like”
wavelets convolved on the subsurface reflectors. The primary difference
between these wavelets is that statistical deconvolution has resulted in a
mixed- vs. deterministic).
The wavelets were extracted deterministically, by cross-correlating
(Wiener-Levinson filter) seismic traces with the known geology derived
from the subsurface well reflection coefficient series. At first glance,
most interpreters would be content having either of these “spike-like”
wavelets convolved on the subsurface reflectors. The primary difference
between these wavelets is that statistical deconvolution has resulted in a
mixed- phase phase  wavelet wavelet (Figure 5 – (Figure 5 –  phase phase spectrum), whereas the
deterministic deconvolution provided the desired broad band, zero spectrum), whereas the
deterministic deconvolution provided the desired broad band, zero  phase phase
 wavelet wavelet . These seemingly minor differences in the . These seemingly minor differences in the  phase phase spectra (Figure
5)
have a significant effect on the seismic data’s overall quality.
Although the “quality” of seismic data has always been in the “eye
of the beholder,” the conversion from mixed- spectra (Figure
5)
have a significant effect on the seismic data’s overall quality.
Although the “quality” of seismic data has always been in the “eye
of the beholder,” the conversion from mixed- phase phase to zero to zero  phase phase provides
a more accurate image of the subsurface geology. provides
a more accurate image of the subsurface geology.
The
reason for the improved accuracy is illustrated in Figure
6. The extracted
wavelets (Figure 5) have been convolved on a single reflector (Top Sand).
Note that the mixed- phase phase  wavelet wavelet has sharp “Pinocchio-like” nose at
the top of the sand, but is followed by a low-frequency “beer-gut.”
When seismic data contains a mixed- has sharp “Pinocchio-like” nose at
the top of the sand, but is followed by a low-frequency “beer-gut.”
When seismic data contains a mixed- phase phase  wavelet wavelet , each reflector has this
“Pinocchio with a beer-gut” character. Neighboring reflectors deeper
in the section (base sand) are , each reflector has this
“Pinocchio with a beer-gut” character. Neighboring reflectors deeper
in the section (base sand) are  phase phase rotated and lose amplitude as their
“noses” are summed with the “beer-guts” from above. rotated and lose amplitude as their
“noses” are summed with the “beer-guts” from above.
The
zero  phase phase  wavelet wavelet ’s sharp “nose” provides a clear image of the top
sand, and its “flat belly” does not interfere with neighboring
reflectors. The comparison of the seismic data in Figures 7 and
8 illustrate typical improvements that are easily obtainable by converting
from mixed- ’s sharp “nose” provides a clear image of the top
sand, and its “flat belly” does not interfere with neighboring
reflectors. The comparison of the seismic data in Figures 7 and
8 illustrate typical improvements that are easily obtainable by converting
from mixed- phase phase to zero to zero  phase phase . Both seismic sections “look” good, and . Both seismic sections “look” good, and
 visual visual advantages can be found in each. In general, however, the seismic
data containing the zero advantages can be found in each. In general, however, the seismic
data containing the zero  phase phase  wavelet wavelet (Figure
8) have a better overall
reflector continuity, better fault definition and more easily identified
stratigraphic relationships. Mixed- (Figure
8) have a better overall
reflector continuity, better fault definition and more easily identified
stratigraphic relationships. Mixed- phase phase wavelets may occasionally tune to
enhance a particular reflector (Figure 7 – increased continuity), but
the overall quality of mixed- wavelets may occasionally tune to
enhance a particular reflector (Figure 7 – increased continuity), but
the overall quality of mixed- phase phase data is lower. data is lower.
The
seismic data comparison for the shallower section is shown in Figure 9.
Return
to top.
Due
to minor earth absorption, the majority of the  wavelet wavelet ’s ’s  phase phase characteristics, as noted above, are derived from the higher frequencies
(20-65 Hertz). The lower frequencies, although contributing less, still
influence the character of the reflectors. The non-zero
characteristics, as noted above, are derived from the higher frequencies
(20-65 Hertz). The lower frequencies, although contributing less, still
influence the character of the reflectors. The non-zero  phase phase components
(5-20 Hertz) of the mixed- components
(5-20 Hertz) of the mixed- phase phase  wavelet wavelet (Figure 9a) can be seen distorting
the image of the geology. (Figure 9a) can be seen distorting
the image of the geology.
These
two images (Figure 9a and b) of the same geology would likely result in
different interpretations. For example, laterally discontinuous reflectors
within the high amplitude package (2.2-2.3 seconds) appear with different
seismic character and even in different locations. Interpretation of them
(channel sands? carbonate mounds?) and their position relative to the
deeper high amplitude reflector (within/below--Figure
9a, or above--Figure 9b) are in question. Knowing that mixed- phase phase wavelets distort the
seismic image, the interpretation should be made from the zero wavelets distort the
seismic image, the interpretation should be made from the zero  phase phase seismic data.
seismic data.
In
general, the zero  phase phase  wavelet wavelet provides a much sharper (broad band - zero provides a much sharper (broad band - zero
 phase phase ) image of the subsurface geology. Stratigraphic relationships above
2.0 seconds (Figure 9) are more clearly defined, and reflector continuity
in general (especially 2.6 seconds) is improved. Deeper in the section (Figure
10), as the earth’s filtering of the higher frequencies
increases, the lower frequencies contribute more strongly to the ) image of the subsurface geology. Stratigraphic relationships above
2.0 seconds (Figure 9) are more clearly defined, and reflector continuity
in general (especially 2.6 seconds) is improved. Deeper in the section (Figure
10), as the earth’s filtering of the higher frequencies
increases, the lower frequencies contribute more strongly to the
 wavelet wavelet ’s ’s  phase phase characteristic (as described above). In the mixed- characteristic (as described above). In the mixed- phase phase seismic data, the non-zero (135 degrees) low-frequency (5-20 Hertz)
components begin contributing more. This adds to the distortion seen
shallow in the section (Figure 9), further reducing the ability to image
the geology accurately.
seismic data, the non-zero (135 degrees) low-frequency (5-20 Hertz)
components begin contributing more. This adds to the distortion seen
shallow in the section (Figure 9), further reducing the ability to image
the geology accurately.
Absorption
also affects the zero  phase phase  wavelet wavelet , reducing high frequencies (narrowing
the bandwidth) and thereby stretching out the , reducing high frequencies (narrowing
the bandwidth) and thereby stretching out the  wavelet wavelet . However, since all
frequencies (5-65 Hertz) are zero . However, since all
frequencies (5-65 Hertz) are zero  phase phase , the seismic image provides an
accurate representation of the geology. , the seismic image provides an
accurate representation of the geology.
The
most striking improvement seen in the zero  phase phase seismic data (Figure
10b)
is the ability to define faults more accurately. The mixed- seismic data (Figure
10b)
is the ability to define faults more accurately. The mixed- phase phase
 wavelet wavelet ’s “beer-gut,” which has grown with depth due to absorption
(loss of high frequencies), is hanging in the fault zones. “Noses” on
the other side of the faults are smeared out by the “beer-guts” from
above. Other significant improvements seen in the zero ’s “beer-gut,” which has grown with depth due to absorption
(loss of high frequencies), is hanging in the fault zones. “Noses” on
the other side of the faults are smeared out by the “beer-guts” from
above. Other significant improvements seen in the zero  phase phase seismic data
are the improved continuity of reflectors and the imaging of geologic
details needed for stratigraphic interpretations. The zero seismic data
are the improved continuity of reflectors and the imaging of geologic
details needed for stratigraphic interpretations. The zero  phase phase  wavelet wavelet ,
as shown in these examples, provides a more accurate image of the
subsurface geology than the mixed- ,
as shown in these examples, provides a more accurate image of the
subsurface geology than the mixed- phase phase  wavelet wavelet . .
Conclusion
Significant
improvements in the quality of seismic data are shown here to be easily
obtainable when wavelets are converted from mixed- phase phase to zero to zero  phase phase by
extracting the by
extracting the  wavelet wavelet and filtering the data. This added effort to
provide seismic data that meets the zero and filtering the data. This added effort to
provide seismic data that meets the zero  phase phase assumption will improve the
accuracy of the interpreted subsurface geology and provide the correct
input to many software packages (Attributes, Amplitudes, AVO) used to
reduce exploration risks. assumption will improve the
accuracy of the interpreted subsurface geology and provide the correct
input to many software packages (Attributes, Amplitudes, AVO) used to
reduce exploration risks.
Return
to top.
|
![]() Click to view this article in PDF format.
Click to view this article in PDF format. Wavelet
Wavelet *
* Wavelet
Wavelet ” in Geophysical Corner, AAPG
Explorer, March, 1997, and “Zero
” in Geophysical Corner, AAPG
Explorer, March, 1997, and “Zero  Phase
Phase Can Aid Interpretation” in
Geophysical Corner, AAPG Explorer, April, 1997. Appreciation is expressed to the author
and to M. Ray Thomasson, former Chairman of the AAPG Geophysical Integration
Committee, and Larry Nation, AAPG Communications Director, for their support of
this online version.
Can Aid Interpretation” in
Geophysical Corner, AAPG Explorer, April, 1997. Appreciation is expressed to the author
and to M. Ray Thomasson, former Chairman of the AAPG Geophysical Integration
Committee, and Larry Nation, AAPG Communications Director, for their support of
this online version.
 Figure
5. These wavelets have been extracted from the seismic in Figures 7 and 8 using the well reflection Coefficients Statistical Deconvolution (a)
commonly produces mixed-
Figure
5. These wavelets have been extracted from the seismic in Figures 7 and 8 using the well reflection Coefficients Statistical Deconvolution (a)
commonly produces mixed- Figure
7. Seismic data identical to Figure 8 other than the method of
deconvolution, Statistical. This seismic data contains the mixed-
Figure
7. Seismic data identical to Figure 8 other than the method of
deconvolution, Statistical. This seismic data contains the mixed- Figure
8. Seismic data identical to Figure 7 other than method of deconvolution,
Deterministic. This seismic data contains the desired zero
Figure
8. Seismic data identical to Figure 7 other than method of deconvolution,
Deterministic. This seismic data contains the desired zero 