![]() Click to view this article in PDF format.
Click to view this article in PDF format.
By David A. Chapin1 and Mark E. Ander1
Search and Discovery Article #40043 (2002)
*Adapted for online presentation from an article by the same authors in AAPG Explorer (February, 1999), entitled “Borehole Gravity: An Old Technique with New Life.” Appreciation is expressed to the author and to M. Ray Thomasson, former Chairman of the AAPG Geophysical Integration Committee, and Larry Nation, AAPG Communications Director, for their support of this online version.
1LaCoste & Romberg, Austin, Texas [email protected]; [email protected]).
|
|
Borehole gravity is a density logging method that has been available for over 30 years – yet today it is a seldom-used technique, even though there are numerous published case studies that demonstrate its value. By one estimate, it is thought that borehole gravity has directly or indirectly contributed to the cumulative discovery of more than one billion barrels of oil equivalent.
The physical principles behind borehole
gravity logging are quite simple. By measuring minute differences in the
earth’s gravity field at different downhole locations, formation
densities can be directly computed. In order to do this, the borehole
gravity
The physics behind this particular
Borehole gravity can easily see beyond casing, cement, hole rugosity and near-borehole formation damage. It works just as effectively in cased holes as it does in open holes. It is a bulk density method, so when coupled with a near-borehole imaging nuclear density method such as a gamma-gamma log, the formation porosity can be computed with great accuracy. Moreover, the pore-filling fluids can often be determined with some reliability. The best results occur with gas vs. liquid, but at higher sensitivities it may be possible to see oil-water contacts.
Figure 1 shows
the gravity
The local gravity field measurements are
directly related to nearby formation densities. It is often asked how
far can the borehole gravity tool “see.” This question is akin to asking
how far can the human eye see. Obviously, the Another question often asked is whether the direction to the object can be determined. Unfortunately, without a multi-well logging program (akin to radio beacon triangulation), this is not currently possible. With single wells it is only possible to determine radial distance away from the borehole, but not direction. Figure 2 shows an example of the distance resolution from borehole gravity. In Case 1, there is no distant porous mass; therefore the near-borehole detecting gamma-gamma log and the far-detecting borehole gravity log show no difference. In Cases 2-4 the distant porous mass is increasingly moved closer to the well bore. The wavelength of the density difference decreases as the amplitude increases. Thus the amplitude and wavelength of the density difference is diagnostic in determining the distance of the remote mass away from the borehole. Notice that this model is sensitive to a distant mass as far away as 200 feet from the borehole. Current uses of the borehole gravity method include formation evaluation, reservoir monitoring, determining behind-casing bypassed gas and exploration for distant structures. Figure 3 shows a conceptual new use of the method for detecting the size and shape of a gas cone from a producing well. Borehole gravity is not only capable of imaging past a gas cone to determine the true top of the gas-oil contact, but it is also capable of determining the shape of the cone, as these models show. Figure 4 shows how borehole gravity can contribute to a gas discovery. A set of actual logs, acquired in 1996, is shown. The deviation between the near-borehole detecting gamma-gamma log and the far-imaging borehole gravity log (in yellow) helped determine that the Cannae #1 well was 300 feet away from a porous reef in the east Texas Cotton Valley trend. Based on this information, the well was sidetracked, and a commercial discovery was made.
Why hasn’t borehole gravity become a more
widespread logging method? This is due primarily to engineering
limitations of the present tool. Currently it must be used in nearly
vertical, large-diameter boreholes, and it takes on average about five
to seven minutes to acquire a data point. The only commercially
available borehole gravity sensors are manufactured by LaCoste & Romberg
of Austin, Texas. LaCoste & Romberg has begun to develop a new borehole
gravity We predict that these advances will lead to renewed interest in the technology from oil and wireline companies. Innovative new uses, such as time-lapse reservoir surveillance and gas storage monitoring, are also expected to generate new demands for the technology. We foresee a day when borehole gravity logs will be as common as any other wireline log. While this technology is old and well-developed, it now has new life. Return to top. |


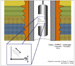 Figure 1: A schematic of the borehole gravity logging tool.
Figure 1: A schematic of the borehole gravity logging tool.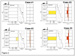 Figure 2: A model of the distance sensitivity of borehole
gravity.(courtesy of L.A. Beyer, adapted from A.K. Shultz).
Figure 2: A model of the distance sensitivity of borehole
gravity.(courtesy of L.A. Beyer, adapted from A.K. Shultz). Figure 4: Measured borehole gravity logs from the Cannae #1 well,
East Texas (courtesy of D.G. Ziegler and Broughton Operating
Corporation).
Figure 4: Measured borehole gravity logs from the Cannae #1 well,
East Texas (courtesy of D.G. Ziegler and Broughton Operating
Corporation).
