![]() Click to view article in PDF format.
Click to view article in PDF format.
GCShaded
Relief in  Display
Display of
of  Seismic
Seismic
 Data
Data *
*
By
Arthur Barnes1
Search and Discovery Article #40097 (2003)
*Adapted for online presentation from the Geophysical Corner column in AAPG Explorer August, 2002, entitled “What a Relief Shade Can Be,” prepared by the author. Appreciation is expressed to the author, to R. Randy Ray, Chairman of the AAPG Geophysical Integration Committee, and to Larry Nation, AAPG Communications Director, for their support of this online version.
1Landmark Graphics, Englewood, Colorado ([email protected].)
In the shaded relief image of Figure 1 you see a
rugged mountain with craters on its flanks. Lunar topography? A stretch of
remote desert on Earth? Hardly – it is a time slice through a  seismic
seismic volume.
Compare this image with Figure 2, a conventional
volume.
Compare this image with Figure 2, a conventional  display
display of the same
of the same  data
data , and
you will agree that shaded relief wonderfully complements standard
, and
you will agree that shaded relief wonderfully complements standard
displays by revealing details and presenting them in a form that geologists
readily appreciate. Yet, already knew that, for shaded relief has been employed
for over a century in displays of topography, and today it is ubiquitous in the
 display
display of any geological or geophysical
of any geological or geophysical  data
data that is presented as a map,
including digital elevations, gravity and magnetic
that is presented as a map,
including digital elevations, gravity and magnetic  data
data , interpreted
, interpreted  seismic
seismic horizons and geologic models. Whatever the application, the motivation for
shaded relief displays is always the same – to transform
horizons and geologic models. Whatever the application, the motivation for
shaded relief displays is always the same – to transform  data
data into
realistic-looking apparent topography and thereby aid interpretation by
revealing or suggesting true geology.
into
realistic-looking apparent topography and thereby aid interpretation by
revealing or suggesting true geology.
|
uShaded
relief and
uShaded
relief and
uShaded
relief and
|
Click to view
sequence of Figures 2 (conventional
Click to view
sequence of Figures 2 (conventional
Shaded Relief and
Why was shaded relief not applied to the
Two reasons stand out:
To apply shaded relief to a 3-D
Shaded relief actually contains the same
information as the common dip-azimuth attribute (Figure 4). This common
information is the reflection dip and azimuth. Shaded relief combines
them into apparent topography, whereas dip-azimuth shows them together
with dip determining the shading of the
While shaded relief replaces dip-azimuth, it
complements other attributes, such as continuity (Figure 5). Both shaded
relief and continuity reveal details hidden in the There is also a difference of directionality, for most attributes reveal structures in all directions, whereas shaded relief is directional, enhancing features perpendicular to the illumination direction while suppressing those that are parallel. As a result, shaded relief displays should be created in pairs with orthogonal illumination directions so as to capture all features. This directionality is useful, as it makes a powerful directional filter of shaded relief, enabling a user to selectively highlight certain trends while hiding others.
|

 Figure 1. A picture of the moon? No, a time
slice through a
Figure 1. A picture of the moon? No, a time
slice through a 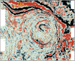 Figure 2. The conventional
Figure 2. The conventional 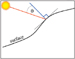 Figure 3. The relative illumination at a point
on a surface is a function of the angle between the incident light and
the surface normal.
Figure 3. The relative illumination at a point
on a surface is a function of the angle between the incident light and
the surface normal.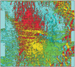 Figure 4. Dip-azimuth corresponding to
Figure 4. Dip-azimuth corresponding to Figure 5. Reflection continuity corresponding
to
Figure 5. Reflection continuity corresponding
to