![]() Click to view page images in PDF format
Click to view page images in PDF format
 GAS
GAS HYDRATES AT THE STOREGGA SLIDE ON THE MID-NORWEGIAN MARGIN
HYDRATES AT THE STOREGGA SLIDE ON THE MID-NORWEGIAN MARGIN
Stefan Bunz*, Jurgen Mienert, and Karin Andreassen
Department of Geology, University of Tromsø, Dramsveien 201, N-9037 Tromsø, Norway
* Tel: +47 77646266, Fax: +47 77645600, Email: [email protected], (Corresponding author)
 Gas
Gas hydrates contain more carbon than does any other global reservoir and are abundant on continental margins worldwide. These two facts make
hydrates contain more carbon than does any other global reservoir and are abundant on continental margins worldwide. These two facts make  gas
gas hydrates important as a possible future energy resource, in submarine landsliding and in global climate change. Particularly on the mid-Norwegian margin, the recognition of inferred
hydrates important as a possible future energy resource, in submarine landsliding and in global climate change. Particularly on the mid-Norwegian margin, the recognition of inferred  gas
gas hydrate occurrence in close proximity to one of the world’s largest submarine landslides has stimulated renewed interest in the role of
hydrate occurrence in close proximity to one of the world’s largest submarine landslides has stimulated renewed interest in the role of  gas
gas hydrates in slope stability and their potential environmental impact through the release of large quantities of methane into the ocean and atmosphere. Therefore, it is necessary (1) to understand the distribution of the
hydrates in slope stability and their potential environmental impact through the release of large quantities of methane into the ocean and atmosphere. Therefore, it is necessary (1) to understand the distribution of the  gas
gas hydrates, (2) to assess the amount of
hydrates, (2) to assess the amount of  gas
gas hydrates and free
hydrates and free  gas
gas that are stored in the reservoir, and (3) to investigate the key mechanisms that occur in this
that are stored in the reservoir, and (3) to investigate the key mechanisms that occur in this  gas
gas hydrate province, e.g.
hydrate province, e.g.  gas
gas migration and accumulation, hydrate formation and the role of the subsurface geological structure and stratigraphy.
migration and accumulation, hydrate formation and the role of the subsurface geological structure and stratigraphy.
Geophysical evidence for  gas
gas hydrates exists along the northern sidewall of the Storegga Slide. A bottom-simulating reflector (BSR) reflects the base of the
hydrates exists along the northern sidewall of the Storegga Slide. A bottom-simulating reflector (BSR) reflects the base of the  gas
gas hydrate stability zone (GHSZ) at about 280 mbsf, and covers an area of approximately 4000
km2, outside but also inside the slide area (Figure
1). Seismic profile NH9651-202 (Figure 2) shows the typical expression of the BSR in the study area. The BSR generally marks the upward termination of enhanced reflections. The amplitude of the enhanced reflections varies considerably along seismic lines in the study area. The distribution of the
hydrate stability zone (GHSZ) at about 280 mbsf, and covers an area of approximately 4000
km2, outside but also inside the slide area (Figure
1). Seismic profile NH9651-202 (Figure 2) shows the typical expression of the BSR in the study area. The BSR generally marks the upward termination of enhanced reflections. The amplitude of the enhanced reflections varies considerably along seismic lines in the study area. The distribution of the  gas
gas hydrates shows three major geological controls: (1) the
hydrates shows three major geological controls: (1) the  gas
gas hydrate stability conditions that exclude
hydrate stability conditions that exclude  gas
gas hydrates on the continental shelf, because bottom-water temperatures are too high, (2) impermeable glacigenic debris flows that define the northern boundary and inhibit upward migration of fluids into the GHSZ, and (3) the intersection of the base of the
hydrates on the continental shelf, because bottom-water temperatures are too high, (2) impermeable glacigenic debris flows that define the northern boundary and inhibit upward migration of fluids into the GHSZ, and (3) the intersection of the base of the  gas
gas -hydrate stability with the base of the Naust formation, because sediments of the underlying Kai formation are not conducive for
-hydrate stability with the base of the Naust formation, because sediments of the underlying Kai formation are not conducive for  gas
gas hydrate growth. As a result of the geological controls the BSR only occurs within the contouritic and hemipelagic deposits of the Naust formation, which seem to be the favorable host sediments for the
hydrate growth. As a result of the geological controls the BSR only occurs within the contouritic and hemipelagic deposits of the Naust formation, which seem to be the favorable host sediments for the  gas
gas hydrates.
hydrates.
A detailed analysis of the  gas
gas hydrate /free
hydrate /free  gas
gas system using ocean-bottom seismometer (OBS) and ocean-bottom cable (OBC)
system using ocean-bottom seismometer (OBS) and ocean-bottom cable (OBC)  data
data allows us to assess the elastic properties of hydrated and gassy sediments and to image the heterogeneous distribution of free
allows us to assess the elastic properties of hydrated and gassy sediments and to image the heterogeneous distribution of free  gas
gas and
and  gas
gas hydrate beneath the seabed. Above the BSR, P-wave velocities that are higher than expected unveil the presence of
hydrate beneath the seabed. Above the BSR, P-wave velocities that are higher than expected unveil the presence of  gas
gas hydrates within the sediments at the northern flank of the Storegga Slide
(Figure 2). Underneath the BSR, P-wave velocities indicate the existence of free
hydrates within the sediments at the northern flank of the Storegga Slide
(Figure 2). Underneath the BSR, P-wave velocities indicate the existence of free  gas
gas . S-wave velocities
. S-wave velocities  obtained
obtained from the OBS
from the OBS  data
data are unaffected by either the presence of hydrates, or the presence of
are unaffected by either the presence of hydrates, or the presence of  gas
gas underneath the BSR
(Figure 2). In addition, a multi-component OBC line exhibits a BSR only on the P-wave component. No P-S reflections are associated with the BSR along this line, indicating that the
underneath the BSR
(Figure 2). In addition, a multi-component OBC line exhibits a BSR only on the P-wave component. No P-S reflections are associated with the BSR along this line, indicating that the  gas
gas hydrate-bearing sediments at the base of the hydrate stability zone are not stiff enough to increase the shear modulus of the sediments to produce P-S converted wave reflections. We conclude that
hydrate-bearing sediments at the base of the hydrate stability zone are not stiff enough to increase the shear modulus of the sediments to produce P-S converted wave reflections. We conclude that  gas
gas hydrates do not cement the sediments, but are rather disseminated in the sediment pore space.
hydrates do not cement the sediments, but are rather disseminated in the sediment pore space.
 Gas
Gas hydrates occur in an approximately 50-m-thick zone above the BSR and average
hydrates occur in an approximately 50-m-thick zone above the BSR and average  gas
gas hydrate concentrations are 3 – 6% of the pore space when modeled by weighted-equation theory or effective-medium theory with hydrates as a component of the sediment-frame. Concentrations are up to 6 to 12% when modeled by effective-medium theory assuming hydrates as a component of the pore-fluid. The thickness of the free-
hydrate concentrations are 3 – 6% of the pore space when modeled by weighted-equation theory or effective-medium theory with hydrates as a component of the sediment-frame. Concentrations are up to 6 to 12% when modeled by effective-medium theory assuming hydrates as a component of the pore-fluid. The thickness of the free- gas
gas zone beneath the BSR is about 80 m on average and
zone beneath the BSR is about 80 m on average and  gas
gas occupies 0.4 – 0.8% of pore volume assuming homogeneous
occupies 0.4 – 0.8% of pore volume assuming homogeneous  gas
gas distribution or up to 18% of pore volume if the
distribution or up to 18% of pore volume if the  gas
gas is assumed to be patchily distributed.
is assumed to be patchily distributed.
The heterogeneous distribution of free  gas
gas and
and  gas
gas hydrate results from the complex interaction between fluid flow pathways, porosity and permeability contrasts, the location of
hydrate results from the complex interaction between fluid flow pathways, porosity and permeability contrasts, the location of  gas
gas seeps and possibly deep-seated hydrocarbon reservoirs.
seeps and possibly deep-seated hydrocarbon reservoirs.  Gas
Gas is predominantly distributed along strata and not along the base of the GHSZ underneath the hydrates. As a result, our
is predominantly distributed along strata and not along the base of the GHSZ underneath the hydrates. As a result, our  data
data show an increase in
show an increase in  gas
gas concentration with depth at certain locations. The
concentration with depth at certain locations. The  gas
gas in the strata significantly increases the impedance contrast causing enhanced reflections on the seismic reflection
in the strata significantly increases the impedance contrast causing enhanced reflections on the seismic reflection  data
data . The reflection enhancement terminates at the level of the base of the GHSZ, where hydrates overly and possibly trap
. The reflection enhancement terminates at the level of the base of the GHSZ, where hydrates overly and possibly trap  gas
gas , causing the BSR to be observed as an envelope of those terminations rather than a distinct reflection. Amplitude anomalies related to the BSR are primarily caused by the
, causing the BSR to be observed as an envelope of those terminations rather than a distinct reflection. Amplitude anomalies related to the BSR are primarily caused by the  gas
gas and not the hydrates.
and not the hydrates.
The Storegga  gas
gas hydrate system appears to be a very dynamic system due to a polygonal fault system that occurs in the sediments underneath the hydrate-bearing sediments. Development of polygonal faults and the related expulsion of formation water might drive the fluid flow in the area.
hydrate system appears to be a very dynamic system due to a polygonal fault system that occurs in the sediments underneath the hydrate-bearing sediments. Development of polygonal faults and the related expulsion of formation water might drive the fluid flow in the area.  Gas
Gas hydrates seem to concentrate directly above the base of the GHSZ, which indicates that
hydrates seem to concentrate directly above the base of the GHSZ, which indicates that  gas
gas hydrates most likely develop from
hydrates most likely develop from  gas
gas -rich fluids that migrate into the GHSZ from sediments below. Deep-seated Tertiary dome structures with inferred hydrocarbon reservoir might be one of the most likely sources of
-rich fluids that migrate into the GHSZ from sediments below. Deep-seated Tertiary dome structures with inferred hydrocarbon reservoir might be one of the most likely sources of  gas
gas . However, the exact origin of
. However, the exact origin of  gas
gas remains for further investigation.
remains for further investigation.
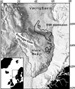 Figure 1. Distribution of a
Figure 1. Distribution of a  gas
gas -hydrate related BSR (outlined in black) on the mid-Norwegian. The most continuous BSR occurs on the northern flank of the Storegga Slide (black dashed
line).S-wave velocities are unaffected by either the presence of hydrates, or the presence of
-hydrate related BSR (outlined in black) on the mid-Norwegian. The most continuous BSR occurs on the northern flank of the Storegga Slide (black dashed
line).S-wave velocities are unaffected by either the presence of hydrates, or the presence of  gas
gas underneath the
underneath the
![]() Figure 2. Example of the BSR on the mid-Norwegian margin. The BSR is mainly identified as the termination of enhanced reflections. The P-wave velocity profile of OBS JM516 shows a clear velocity inversion at the depth of the
BSR. Higher velocity above the BSR indicates the presence of
Figure 2. Example of the BSR on the mid-Norwegian margin. The BSR is mainly identified as the termination of enhanced reflections. The P-wave velocity profile of OBS JM516 shows a clear velocity inversion at the depth of the
BSR. Higher velocity above the BSR indicates the presence of  gas
gas hydrates; lower velocity underneath the BSR provides evidence for the presence of free
hydrates; lower velocity underneath the BSR provides evidence for the presence of free  gas
gas within the sediments. S-wave velocities are unaffected by either the presence of hydrates, or the presence of
within the sediments. S-wave velocities are unaffected by either the presence of hydrates, or the presence of  gas
gas underneath the
BSR. Therefore, we conclude that
underneath the
BSR. Therefore, we conclude that  gas
gas hydrates do not cement the sediments, but are rather disseminated in the sediment pore space.
hydrates do not cement the sediments, but are rather disseminated in the sediment pore space.
