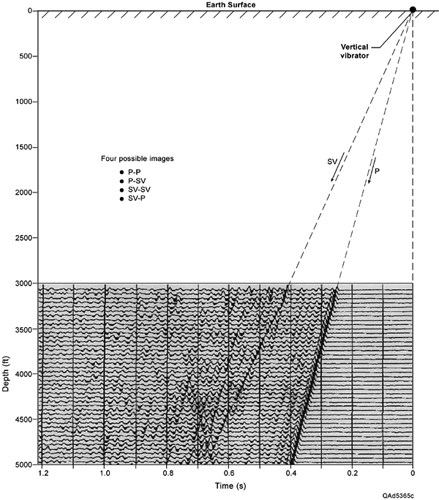
Click image to view enlargement.
Figure 2. VSP data showing downgoing P and SV modes produced by a vertical vibrator. In this example,
the vibrator was close to the vertical well in which the downhole geophones were deployed, which would
be a near-vertical take-off angle such as β in Figure 1. Across the depth interval 3,000 to 5,000 feet, the
velocity of the downgoing P wave is approximately 13,300 ft/s, and the velocity of the downgoing SV
mode is approximately 8,000 ft/s. If long data traces are recorded, there is the potential to construct four
images (P-P, P-SV, SV-SV, SV-P), where the first term defines the downgoing wavefield and the second
term identifies the upgoing wavefield.