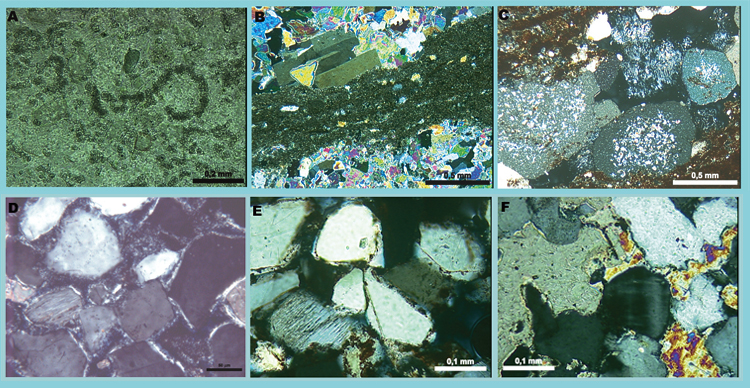
Figure 4. (A) Micro-rhombic dolomite replacing originally microbial, micritic mud, being replaced by anhydrite (10x, parallel polarizers
PPL – 897.05); B) Microdolomite and anhydrite replacing the original, laminated sandy micritic mud (5x, crossed polarizers XLP – 897.05);
(C) Anhydrite inclusions occur within gypsum and calcite-gypsum nodules (5x, XLP – 178.04); D) Undifferentiated clay coatings covered
by clay rims in the fluvial sandstones (40x, PPL – 123.78); ); (E) Quartz overgrowth engulfing hematite coatings in sandstone (20x,
PPL – 689.35); (F) Poikilotopic calcite replacing intergranular anhydrite cement (20x, XPL – 821.78).
