![]() Click to view poster in PDF format.
Click to view poster in PDF format.
PSAutomatic
Detection of the Degree of Compaction in Reservoir Rocks Based on  Visual
Visual Knowledge*
Knowledge*
Carlos Eduardo Santin1, Mara Abel2, Karin Goldberg3 and Luiz Fernando De Ros3
Search and Discovery Article #80061 (2009)
Posted October 15, 2009
* Adapted from poster presentation at AAPG Annual Convention and Exhibition, Denver, Colorado, USA, June 7-10, 2009.
1Endeeper Rock Knowledge Systems, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil ([email protected])
2Institute of Informatics, UFRGS, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil
3Petroleum Geology Program, UFRGS, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil
A
low-cost method is proposed for evaluating the degree of compaction in
reservoir rocks by using automatic inference methods on optical
photomicrographs. In order to reproduce the  visual
visual interpretation performed
during petrographic analysis, a hybrid method was developed combining
image-processing algorithms with knowledge representation and reasoning models.
The method proposed was inspired on
interpretation performed
during petrographic analysis, a hybrid method was developed combining
image-processing algorithms with knowledge representation and reasoning models.
The method proposed was inspired on  visual
visual attention, the mechanism used
by the human brain for dealing with
attention, the mechanism used
by the human brain for dealing with  visual
visual information. This mechanism allows
the brain to filter the huge amount of information that comes through the eyes,
selecting the relevant elements to be further analysed by the highly abstract
level of reasoning. The process involves the decomposition of scenes, and the
competition among their different aspects in order to isolate and select the
relevant areas. In other words, the eyes of petrographers initially examine a
thin-section by capturing and isolating the grains borders (outlines), and then
focus on the grains. The outlines are essential to separate each grain from
other grains and their interstices, because petrographic analysis is performed
in the two-dimensional universe of thin-sections. The knowledge at this level
is modelled in terms of Sections (grains), Outlines (borders of
grains), and Interstices, which may be Pores (empty) or NonPores (e.g. cement, matrix). The shapes of the outlines (mainly concave or
convex), complemented by the detection of the impregnation blue resin,
indicates if they contain Pores, NonPores or Sections. The
types of contacts between grains are then used to define the degree of
compaction of the rocks. The system provides a preliminary identification of
the objects that can be interactively refined by the user when the grain
outlines are unclear in the images. The evaluation of compaction degree
provided by this method is far more sensitive and precise than those based on
the intergranular volume or number of intergranular contacts. This formalized
interpretation method shows better results for the complex tasks of reservoir
quality characterization and prediction.
information. This mechanism allows
the brain to filter the huge amount of information that comes through the eyes,
selecting the relevant elements to be further analysed by the highly abstract
level of reasoning. The process involves the decomposition of scenes, and the
competition among their different aspects in order to isolate and select the
relevant areas. In other words, the eyes of petrographers initially examine a
thin-section by capturing and isolating the grains borders (outlines), and then
focus on the grains. The outlines are essential to separate each grain from
other grains and their interstices, because petrographic analysis is performed
in the two-dimensional universe of thin-sections. The knowledge at this level
is modelled in terms of Sections (grains), Outlines (borders of
grains), and Interstices, which may be Pores (empty) or NonPores (e.g. cement, matrix). The shapes of the outlines (mainly concave or
convex), complemented by the detection of the impregnation blue resin,
indicates if they contain Pores, NonPores or Sections. The
types of contacts between grains are then used to define the degree of
compaction of the rocks. The system provides a preliminary identification of
the objects that can be interactively refined by the user when the grain
outlines are unclear in the images. The evaluation of compaction degree
provided by this method is far more sensitive and precise than those based on
the intergranular volume or number of intergranular contacts. This formalized
interpretation method shows better results for the complex tasks of reservoir
quality characterization and prediction.
|
uCompaction Evaluation of Siliciclastic Rocks uKnowledge Modelling of
uCompaction Evaluation of Siliciclastic Rocks uKnowledge Modelling of
uCompaction Evaluation of Siliciclastic Rocks uKnowledge Modelling of
uCompaction Evaluation of Siliciclastic Rocks uKnowledge Modelling of
uCompaction Evaluation of Siliciclastic Rocks uKnowledge Modelling of
uCompaction Evaluation of Siliciclastic Rocks uKnowledge Modelling of
uCompaction Evaluation of Siliciclastic Rocks uKnowledge Modelling of
|
The quality of a rock as a petroleum reservoir is strongly affected by the post-depositional (diagenetic) processes that modify the original porosity and permeability of the sediments. Petrographic analysis allows the capture of relevant aspects for determining the depositional and diagenetic history and for understanding how the sequence of processes has affected reservoir quality. Petrographic descriptions provide fundamental information for petroleum exploration and production.
In the last years we have developed a software suite named
Petroledge® that allows the acquisition and management of detailed
petrographic information of siliciclastic and carbonate reservoir rocks.
Petrographic information is selected and modelled based on
In this paper, we explain how the Petroledge® suite was
improved in order to provide the evaluation of compaction degree of
reservoirs by using optical photomicrographs and inference methods. In order
to reproduce the geological
Compaction Evaluation of Siliciclastic Rocks
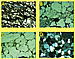
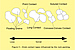
The quality of a rock as a petroleum reservoir is essentially defined by its porosity and permeability values. Basically, three diagenetic processes are responsible by the modification of the intergranular volume from clastic rocks during burial: mechanical compaction, chemical compaction and cementation. (Figure 1) The mechanical compaction causes the reduction of the intergranular volume by rearrangement, fracturing or ductile deformation of the grains. Chemical compaction reduces the intergranular volume by dissolving the grains along their contacts. Cementation causes obstruction of the intergranular pores by the precipitation of new minerals, mostly without reducing the intergranular volume. The intensity of mechanical and chemical compaction defines the degree of proximity – or packing – of the grains, which can be loose, normal or tight. As the packing changes from loose to tight, the types of contacts between grains change from point contact, to long, to concaves-convex and to sutured (Taylor, 1950). (Figure 2)
Other method for evaluating the degree of compaction involves comparing the present intergranular volume (IGV) with the original IGV, measured using the grain size and selection (Beard and Weyl 1973). Based on these parameters, the degree of compaction is calculated considering how much of the original IGV was lost during burial. Samples with less than 50% of reduction of the original intergranular volume are considered loosely packed, while those with more than 70% of IGV reduction are considered tightly packed, with normally packed samples in the interval between these values.
Our system performs the evaluation of compaction degree based on the number and types of contacts detected in optical photomicrographs and described by user, as well as on the evaluation of intergranular volume. Table 1 shows examples of inputs and outputs of the system, for two samples with different degree of compaction.
Knowledge
Modelling of
In order to identify evidence for image interpretation in
the physical level to be used to support the reasoning process in the
knowledge level, we propose a knowledge representation model in three levels
of abstraction, summarized in Figure 3. In
the first one, the Image Processing Level, we have the basic elements of the
image, which are pixels and image entities. (Figure
4) Each image is referenced to a spatial coordinate system that
preserves a real correspondence with the rock thin section. The
correspondence is controlled by an electromechanical microscope stage
(Victoreti, Abel et al., 2007) developed to help in the point-counting for quantitative
petrographic analysis. The processing in the lower level starts with the
image segmentation using a
In the
The objects captured and
labelled in the
A domain ontology is a formal representation of the consensual meaning of the objects in a particular domain (Gómez-Pérez, Fernández-López et al., 2004). Ontologies are being used to define a standard vocabulary and to formalize the shared meaning of it in such a way that it can be understood and applied by computers. Ontologies have been shown a strong approach in representing the knowledge used to support automatic inference processing in expert system or to be shared through the WEB (e.g. to support e-commerce, semantic search based on geological ontologies such as in (Mello, Abel et al., 2007)).
The
identities of the objects in each level are guaranteed by mapping tables that
associate the primitives of each level of representation, such as, Section in the
Our inference mechanism
receives the rock image, the segmented image and the size scale. The sections
in the segmented image are individualized, and the main shape, concave or
convex, is determined. Grains, defined by their convex shapes are identified,
and their largest axes are measured. Pores are identified by the blue resin
colour. After the physical processing of the image, the elements are
associated to the objects in the
The workflow at Figure 7 shows how the data processing is done in our approach, since the rock description using the Petroledge® system until the inference of compaction degree.
The automatic interpretation of
We use this approach in order to interpret the level of compaction of petroleum reservoirs, based on photomicrographs collected during petrographic description. Since our approach is based on the shape of the contact between grains, it is not affected by the common deformations of the image caused by optical capture. These deformations, such as the parallax, that augment the area of the grains as far as are the grains from the center of the optical system, invalidate direct measures over the image.
Although the system occasionally requires human intervention in some critical steps, such as to improve the segmentation of the images, it significantly reduces the time of the process applying a low-cost algorithm in terms of processing, while allowing a formalization and implementation of a very subjective method. A formalized interpretation method supports better correlation of the results along with the complex tasks of characterization and prediction of the quality of petroleum reservoirs.
We acknowledge the support of the Brazilian Research Council (CNPq) and Agency for Studies and Projects Funding (FINEP).
Abel, M., L.A.L. Silva, J.A.
Campbell, and L.F. De Ros, 2005, Knowledge acquisition and interpretation
problem-solving methods for
Acharayya, M., R.K. De, and M.K.
Kundu, 2003, Segmentation of Remotely Sensed Images Using
Beard, D.C. and P.K. Weyl, 1973, Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand: AAPG Bulletin, v. 57/2, p. 349-369.
De Ros, L.F., M. Abel, and K. Goldberg, 2007, Advanced Acquisition and Management of Petrographic Information from Reservoir Rocks Using the PETROLEDGE®System: AAPG Annual Convention and Exhibition. Long Beach, CA. Search and Discovery Article #90063 (2007). Web accessed 09 Sept 2009.
Gómez-Pérez, A., M. Fernández-López, and O. Corcho, 2004, Ontological Engineering: With examples from the areas of knowledge management, e-commerce and the Semantic Web: Springer, 403 p.
Le Meur, O., Le Callet, P., D.
Barba, and D. Thoreau, A coherent computational approach to model bottom-up
Mello, M.T., M. Abel, and F. Garcia-Sanchez, 2007, Using Semantic Web Services to Integrate Data and Processes from Different Web Portals: International Workshop on Intelligent Web Based Tools. Patras, Grecia: CEUR. October 29-31, p. 9-16.
Taylor, J.M., 1950, Pore-space Reduction in Sandstones: AAPG Bulletin, v. 34/4, p.701-716.
Victoreti,
F.I., M. Abel, L.F. De Ros, M.M. Oliveira, 2007, Documenting
|