![]() Click to view article in PDF format.
Click to view article in PDF format.
GCVertical Seismic Profiling at Eldfisk Field *
Bob Hardage1
Search and Discovery Article #40389 (2009)
Posted February 20, 2009
*Adapted from the Geophysical Corner column, prepared by the author, in AAPG Explorer, June, 2008, and entitled “Questions?  VSP
VSP May Have Answers”. Editor of Geophysical Corner is Bob A. Hardage. Managing Editor of AAPG Explorer is Vern Stefanic; Larry Nation is Communications Director.
May Have Answers”. Editor of Geophysical Corner is Bob A. Hardage. Managing Editor of AAPG Explorer is Vern Stefanic; Larry Nation is Communications Director.
1Bureau of Economic Geology, The University of Texas at Austin ([email protected])
General Statement
Vertical seismic profiling ( VSP
VSP ) began to be popular among non-Soviet scientists in the late 1970s, about the time that my previous employer, Phillips Petroleum Company, and our partners were trying to determine development strategies for newly discovered fields in the Greater Ekofisk area of the Norwegian North Sea. Resource evaluations and development planning at Ekofisk and Eldfisk had to be done with 2-D seismic data at that time – and one of the controversies regarding development of these fields centered on the famous “collapsed zone” atop each structure.
) began to be popular among non-Soviet scientists in the late 1970s, about the time that my previous employer, Phillips Petroleum Company, and our partners were trying to determine development strategies for newly discovered fields in the Greater Ekofisk area of the Norwegian North Sea. Resource evaluations and development planning at Ekofisk and Eldfisk had to be done with 2-D seismic data at that time – and one of the controversies regarding development of these fields centered on the famous “collapsed zone” atop each structure.
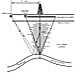
One 2-D seismic profile of 1970s vintage that crosses Eldfisk field is displayed here as Figure 1 and shows a classic example of the apparent collapsed structural crest that had to be factored into early field development plans. Two camps existed among the partner teams that had to decide how to proceed with development drilling:
Camp 1 said, “The anticline has a true collapsed top and reserves are reduced.”
Camp 2 said, “There is a low-velocity chimney in the thick shale above the structure that creates a velocity pull down and there is no collapsed top.”
Camp 1 wanted to interpret a fault where one is drawn on the profile; Camp 2 believed that there was no fault, just a velocity-generated time sag.
| uConclusion |
|
||||||
uConclusion |
|