Click to view article in PDF
format
Click to view article in PDF
format
GCMulti- Azimuth
Azimuth Seismic for Sub-Salt Targets*
Seismic for Sub-Salt Targets*
Bob Hardage1
Search and Discovery Article #40381 (2009)
Posted January 14, 2009
*Adapted from the Geophysical Corner column, prepared by the author, in AAPG Explorer, December, 2008, and entitled “Results Shine for New Technology”. Editor of Geophysical Corner is Bob A. Hardage. Managing Editor of AAPG Explorer is Vern Stefanic; Larry Nation is Communications Director.
1Bureau of Economic Geology, The University of Texas at Austin ([email protected])
One technical barrier plaguing hydrocarbon exploration is the inability to see geologic targets below distorted salt layers that span large areas of numerous depositional basins. The complex geometrical shapes of most salt bodies distort trajectories of seismic raypaths to such an extent that uniform illumination of sub-salt targets cannot be achieved with conventional seismic technology. If there is no uniform illumination of a target, a seismic image of that target cannot be correct. A new technology that addresses this problem of non-uniform illumination of sub-salt targets is a concept called multi- azimuth
azimuth data acquisition.
data acquisition.
|
Imaging MethodsAs shown in Figure 1, a hypothetical salt trend is imaged with three cable tows that traverse the area in three different
· One possibility is shown as Figure 2a. In this option, data are acquired with a narrow-
· A second data-acquisition scheme, illustrated in Figure 2b, involves multiple vessels that generate wider-
If this
Examples
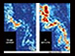
Examples of the increased geological information provided by multi-
The example in Figure 4 is across Mad Dog Field in the Gulf of Mexico. The improvements in data quality and in image detail when multi-
Conclusions
Industry interest in multi-
· Improve the overall signal-to-noise ratio of sub-salt data. · Allow better removal of diffraction noise. · Create a more uniform illumination of targets below layers that distort raypath distributions. · Increase lateral resolution of data. · Produce more accurate amplitude attributes. · Provide better attenuation of multiples.
Any one of these factors is a significant improvement in seismic technology. Collectively, this list forms a compelling reason to implement multi-
References
Keggin, J., T. Manning, W. Rietveld, C. Page, E. Fromyr, and R. van Borselen, 2006, Key aspects of multi-
Michell, S., E. Shoshitaishvili, D. Chergotis, J. Sharp, and J. Etgen, 2006,
|