![]() Click to view article in PDF
format.
Click to view article in PDF
format.
Seismic Characterization of the First 3D Surveys Offshore Cyprus and Lebanon*
Øystein Lie1 and Mark Trayfoot1
Search and Discovery Article #10194 (2009)
Posted May 22, 2009
*Adapted from oral presentation at AAPG International Conference and Exhibition, Cape Town, South Africa, October 26-29, 2008
1Petroleum Geo-Services, Oslo, Norway (mailto:[email protected] )
The
first 3D seismic data in the deep  water
water offshore Cyprus and Lebanon have been
acquired, processed and interpreted. Pre-stack time migration was applied and
the 3D data sets have high signal to noise-ratio and very high
offshore Cyprus and Lebanon have been
acquired, processed and interpreted. Pre-stack time migration was applied and
the 3D data sets have high signal to noise-ratio and very high  reflectivity
reflectivity at
both shallow and deep levels. Despite the lack of exploration well data, a
consistent chronostratigraphic framework has been built across Cyprus and
Lebanon and implications for prospectivity assessed. Several petroleum systems
were identified, and potential prospect types include four-way dip closure
structures and stratigraphic traps. Direct hydrocarbon indicators, including
amplitude and frequency anomalies, are associated with many of the identified
prospects. Amplitude maps have been extracted on offset stacks, and a good
correlation between amplitude anomalies and the closures was found. The recent
3D seismic is considered to reduce the exploration risk in this unexplored
frontier area.
at
both shallow and deep levels. Despite the lack of exploration well data, a
consistent chronostratigraphic framework has been built across Cyprus and
Lebanon and implications for prospectivity assessed. Several petroleum systems
were identified, and potential prospect types include four-way dip closure
structures and stratigraphic traps. Direct hydrocarbon indicators, including
amplitude and frequency anomalies, are associated with many of the identified
prospects. Amplitude maps have been extracted on offset stacks, and a good
correlation between amplitude anomalies and the closures was found. The recent
3D seismic is considered to reduce the exploration risk in this unexplored
frontier area.
|
The offshore areas of
Cyprus and Lebanon in the eastern Mediterranean Sea are currently unexplored
with respect to hydrocarbon resources. The first 3D seismic surveys were
acquired to obtain an improved understanding of the geological structures and
the petroleum potential in these frontier deep
Two areas considered highly
prospective were selected for acquisition of the 3D seismic data. The
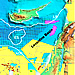
surveys were acquired late 2006/early 2007 and cover approximately 1550km²
(Phase 1 to the south) and 1350km² (Phase 2 to the north) (Figure 1). Phase 1 covers the central part of the
Levantine Basin. Phase 2 covers the northern part of the basin, the Latakia
Ridge, and several other large Syrian- and Cyprus-Arc deformation folds. The
pre-stack time migrated 3D seismic data sets have a high signal to
noise-ratio and a very high
Seismic Interpretation and Hydrocarbon Plays
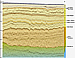
Nine key regional horizons have been interpreted to evaluate the prospectivity of the area. By tying the key reflectors from Cyprus in the west to Lebanon in the east a consistent chronostratigraphy was established. The following horizons were interpreted; Seabed, Intra Pliocene, Base Pliocene, Base Messinian Evaporite, Upper Miocene, Mid Miocene, Base Miocene, Eocene Unconformity and Senonian Unconformity (Figure 2).
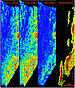
The area contains a number of potential hydrocarbon plays and a variety of structural and stratigraphic trapping styles exist. The Upper Miocene Messinian Evaporite Formation which forms a regional cap rock in the eastern Mediterranean Sea is well developed, and intra-formational seals could also be present within the Cretaceous and Tertiary sequences. Source rock intervals proven onshore Lebanon within the Jurassic, Cretaceous and Paleogene (Beydoun, 1988) are postulated to continue offshore and vertical hydrocarbon migration can be expected along numerous fault planes. Multiple clastic and carbonate horizons in the Jurassic, Lower and Upper Cretaceous, Paleogene and Neogene represent potential reservoir intervals. Prospect TypesSeismic interpretation has delineated large, four-way dip closure structures, and stratigraphic traps. The large four-way dip closure structures in the Phase 1 survey area trend NNE-SSW, parallel to the structural trends observed onshore Lebanon, whereas large transpressional structures further north in the Phase 2 survey trend NE-SW (Figure 3). One such structure, the Latakia Ridge, exhibits a complex structural evolution whereby normal extensional faults were subsequently reactivated during later compressional tectonic phases. The largest sub-salt structural closure in the Levantine Basin is approximately 200km², and depth conversion using interval velocities indicates that the vertical relief is in the order of 200m to 350m.Potential
stratigraphic traps include Miocene(?) onlap and pinchout, deepwater
turbidite fans, incised channels and Late-Cretaceous(?) carbonate build-ups.
The carbonate build-ups could have excellent porosities and permeabilities
and would represent a new play type for deep
|