Click to view article in PDF format.
Click to view article in PDF format.
Understanding Reservoir Architecture: Combining Continuous
Fluid Facies Mapping,  Pressure
Pressure Measurements, Downhole Fluid Analysis, and
Geochemical Analyses*
Measurements, Downhole Fluid Analysis, and
Geochemical Analyses*
By
Daniel McKinney1, Hani Elshahawi1, Matthew Flannery1, Mohamed Hashem1, Lalitha Venkatramanan2, and Oliver Mullins2
Search and Discovery Article #40229 (2007)
Posted February 4, 2007
*Adapted from extended abstract prepared for presentation at AAPG 2006 International Conference and Exhibition, Perth, Australia, November 5-8, 2006
1Shell International, E&P, Houston, TX
2Schlumberger Oilfield Services, Houston, TX
Introduction
Identifying compartmentalization and understanding reservoir structure are of
critical importance to reservoir development. Traditional methods of identifying
reservoir compartmentalization, such as drill stem tests and extended well
tests, often become impractical in deepwater settings with costs approaching the
costs of new wells and emissions becoming increasingly undesirable. Thus,
 compartments
compartments often have to be identified by some other means. Identification of
reservoir compartmentalization by
often have to be identified by some other means. Identification of
reservoir compartmentalization by  pressure
pressure gradient analyses, downhole fluid
analysis (DFA), and geochemical fingerprinting are all means for identifying
barriers, with DFA being a recently introduced novel approach. Independently,
each technique has its limitations, but, together, they are a powerful tool for
providing insights into reservoir architecture. This paper presents two case
studies where the authors have used these techniques in a single well
penetration (i.e., vertical barrier identification) and comparison of data in
two wells in the same structure (i.e., lateral variability).
gradient analyses, downhole fluid
analysis (DFA), and geochemical fingerprinting are all means for identifying
barriers, with DFA being a recently introduced novel approach. Independently,
each technique has its limitations, but, together, they are a powerful tool for
providing insights into reservoir architecture. This paper presents two case
studies where the authors have used these techniques in a single well
penetration (i.e., vertical barrier identification) and comparison of data in
two wells in the same structure (i.e., lateral variability).
|
|
Case I: Assessment of Vertical Barriers in a Single Well Penetration
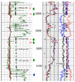
Figure 1 displays
the gamma ray, resistivity and formation Several interesting features are observed in Table 1. First, F and G appear to have similar fluid density, whereas an apparent fluid density inversion between fluids G and J is observed. Second, a gentle fluid compositional grading is observed with the GOR varying gradually from fluid F to fluid I. Lastly, although the GORs computed from downhole spectra are about 15% lower than the true GORs computed in the lab (last column), the trend in the downhole GORs matches the trend observed in the measured GORs.
Application of Fluid Comparison Algorithm (FCA
described by Venkatramanan et al., 2006, and H. Elshahawi et al.,
2006) to analyze fluids G and J showed that
the fluid density inversion is statistically significant with
probability 0.99.
The gentle composition or GOR gradient seen between fluids J, H, and I is expected for an oil column in vertical communication. Open-hole logs suggest that this vertical span is fairly homogeneous. Analysis of gradient densities is in agreement with this assessment. It is suggested that this part of the well is in vertical communication. 13C/13C ratio determination on the mud-gas methane isotopes across this interval supports this interpretation; a clear increase in isotopic trend with depth suggests increasing contribution from thermogenic-sourced methane (Figure 2). The gradual decline in methane concentration in the mud-gas indicates wetness increasing with depth with no step-changes, supporting the gradual density gradient observed by the MDT. The confirmation of vertical compartmentalization between G and J and a compositional gradient between J and I directly impacts reservoir modeling, reserves booking, and development planning. Drainage projections and reserve calculations cannot treat the whole interval as a continuous unit, and scope for recovery could be significantly reduced. Gas injection and water-flood scenarios would have to treat each zone independently, increasing design complexity and cost, while reducing sweep volume and time-to-water break-through. The compositional gradient in the lower reservoir likely extends downdip from the penetrated zone, and topsides facility design plans will have to anticipate production that will drop in GOR with time, even before depletion drive is exhausted. Medium- and long-term economic decisions can hence be revised at a much earlier stage of exploration.
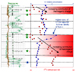
Case II: Cross Well Application. Figure 3 displays a well schematic cartoon of Case II. In this example, there are two suspected flow-barriers that intersect the main borehole and side-track, as illustrated in Figure 4. To test the presence of these barriers, the formation testing and sampling tool was run with two probes positioned to straddle the suspected barrier. The top probe was used to pump fluid above the suspected barrier and the bottom probe was used to assay fluid below the suspected barrier. Application of FCA to analyze fluids in the main borehole led to a probability matrix shown in Table 2. As a rule of thumb, when the output probability of FCA is less than 0.5, we classify the two fluids being compared as being “statistically similar,” referring to downhole optical fluid properties being within the error-bar of the measurement. When the probability is between 0.5 and 0.95, the fluids are classified as “statistically indeterminate”, referring to the lack of clear optical distinction between the two fluids. From the probability matrix in Table 2, we infer that fluids #1A and #1B (across the top suspected barrier, see Figure 4) are statistically similar to each other. Similarly, fluids #2A and #2B and fluids #3A and #3B are statistically similar to each other. The differences between fluids #1B and #2B, which are above the second barrier, and fluids #3A and #3B, which are below the second barrier, are statistically indeterminate. Fluid differences (if any) can only be distinguished from other measurements.
Geochemical fingerprinting, which has
similarities to the FCA methodology by comparing variations in fluid
compositions, confirms these observations.
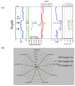
Figure 5A shows that the two fluid samples collected in the original
hole are nearly identical to one another on the spider plot. In
addition, Application of FCA to analyze fluids in the side-track yields the probability matrix shown in Table 3. Again, the fluids assayed in the side-track are statistically similar to each other in their optical properties.
The fluids in the main-hole (first column) are
compared to fluids in the side-track (first row) in
Table 4. In this case, because different
spectrometers were used to assay the fluids downhole, a larger
uncertainty in the measurement ( e
s = 0.02) was used in data analysis
with FCA. Again, though, geochemical fingerprinting between fluids
collected in the original hole and side-track are nearly identical (Figure
5B). Also, statistical analysis of the
Summary
A practical problem that most oil companies
face is determining the number of sampling stations because of the
associated cost. They need to know if fluid A is different from fluid B
before committing themselves to sampling and further detailed analysis
in the laboratory. Careful
ReferencesElshahawi, H., L. Venkataramanan, D. McKinney, M. Flannery, O.C. Mullins, and M. Hashem, 2006, Combining continuous fluid typing, wireline formation tester, and geochemical measurements for an improved understanding of reservoir architecture, during SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 24-27 September, San Antonio, Texas, USA: SPE Paper No. 100740-MS. Venkataramanan, L., H. Elshahawi, D. McKinney, M. Flannery, and M. Hashem, and O.C. Mullins, 2006, Downhole fluid analysis and fluid comparison algorithm as an aid to reservoir characterization, during SPE Asia Pacific Oil & Gas Conference and Exhibition, 11-13 September, Adelaide, Australia: SPE Paper No. 100937-MS.
|