![]() Click to view page images in pdf format.
Click to view page images in pdf format.
 Digital
Digital )
)
7th Middle East Geosciences Conference and Exhibition
Manama, Bahrain
March 27-29, 2006
Saudi Aramco
In pursuit of structural imaging and stratigraphic understanding of a producing Jurassic carbonate
reservoir, Saudi Aramco is acquiring 1300 km2 of 3D transition seismic data. Challenges begin with the
variety of topographies including sand dunes, sabkhas, transition zone marshes, shorelines, and shallow
water depths finishing with deeper marine zones. In addition, the land portions contain very densely
populated towns, large agricultural areas and huge power plants. All of these issues demand the
application of critical and accurate steps in order to ensure a seamless product free of false structures
and  processing
processing artifacts.
artifacts.
The acquisition includes four independently configured source types; dynamite, vibrator, shallow and
deep air gun. Associated with these are the different seismic receiver types; geophones, marsh phones,
hydrophones and dual sensors, Figure 1. These produce an extremely complex  processing
processing environment,
with unique challenges which must be met before producing a final volume for successful interpretation.
This unique multi-environment
environment,
with unique challenges which must be met before producing a final volume for successful interpretation.
This unique multi-environment  processing
processing task requires instrument matching, source matching, dual
sensor summation, generation of datum statics corrections for various source and receivers, noise
handling for different conditions, velocity analysis, and pre-stack time migration. The time slice
extraction from the final volume, Figure 2, shows no source or receiver footprint due to the irregular
shooting geometry and transition zone conditions.
task requires instrument matching, source matching, dual
sensor summation, generation of datum statics corrections for various source and receivers, noise
handling for different conditions, velocity analysis, and pre-stack time migration. The time slice
extraction from the final volume, Figure 2, shows no source or receiver footprint due to the irregular
shooting geometry and transition zone conditions.
This paper will show how the integration of all the different variables in  processing
processing produces a final
migrated dataset suitable for the interpretation objectives.
produces a final
migrated dataset suitable for the interpretation objectives.

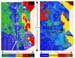 Figure 1. Aerial Distribution of
Source and Receiver Types.
Figure 1. Aerial Distribution of
Source and Receiver Types.