Click to view article
in PDF format.
Click to view article
in PDF format.
The Rio Doce Canyon System in the Northern Espirito Santo Basin, Offshore Brazil: A Model for Interpreting Ancient Deep-Water Sand Transportation Fairways*
By
Brush, Eugene1, Joseph C. Fiduk1, Frank Love2, Peter Gibbs3, Stiig Brink-Larsen4, and George Farrow5
Search and Discovery Article #30028 (2004)
*Adapted from extended abstract for presentation at AAPG Annual Convention, Dallas, TX, April 18-21, 2004.
1CGG Americas, Houston, TX; ([email protected]; [email protected])
2Shell International E & P, Houston, TX ([email protected])
3CGG Consultant, Kent, UK ([email protected])
4Long Island Exploration, Roeyken, Norway ([email protected])
5Consultant, Strathblane, UK.
Abstract
The Rio Doce is one of two modern deep-water canyon
systems found in the Northern Espiritos Santo Basin, Offshore Brazil. It has
been mapped using 3D seismic data covering approximately 10,600 sq km. The
system is north-south trending and extends over 150 km south of the shelf margin
canyon incision through which a modern river feeds sediment into the system.
Seismic  interpretation
interpretation suggests that the Rio Doce system has been active
throughout the Cenozoic and seismic amplitudes suggest that it is a sand-rich
system. It is possible that the Rio Doce system can be tracked back into the
Cretaceous section and linked to the ancient Regencia Canyon system.
suggests that the Rio Doce system has been active
throughout the Cenozoic and seismic amplitudes suggest that it is a sand-rich
system. It is possible that the Rio Doce system can be tracked back into the
Cretaceous section and linked to the ancient Regencia Canyon system.
The second canyon system trends northwest-southeast and
does not have a river feeding sediments into the system. The canyon is growing
toward the shelf by headward erosion. Retrogressive slumping of the canyon walls
and occasional debris  flows
flows from the shelf margin are the primary sources of
sediment for this system. An assessment of seismic amplitudes suggests that this
system is mostly sand-poor.
from the shelf margin are the primary sources of
sediment for this system. An assessment of seismic amplitudes suggests that this
system is mostly sand-poor.
Using the two modern canyon systems as analogs, it is possible to develop a model for deep-water sediment fairways in the Cretaceous and potentially to predict which are sand-rich and which are sand-poor. Ideally, the methodology would involve the combined use of sequence stratigraphy, seismic attribute analysis, and depth imaging.
|
|
IntroductionDeveloping
models for the transport and deposition of sand into the deep-water
environment of various basins around the world is challenging. A model
that fits data in one basin may not
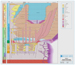
ResultsUsing over 10,600 sq km of 3D seismic data, unconformity-bound seismic mega-sequences from the basement rift to the seafloor in the Espirito Santo Basin were mapped (Figure 1). Sequences were then divided into groups that related to the Cenozoic canyon systems (Rio Doce and an east-west canyon system) or the Cretaceous canyon system (Regencia Canyon). Within the shallow Cenozoic section, both seismic resolution and frequency content are much higher than in the Cretaceous. Beds/seismic events down to 5m in thickness can be resolved. In the deeper Cretaceous section, no beds/ seismic events smaller than approximately 18 meters thick can be resolved. The phase of all the seismic is zero phase SEG reverse polarity. Sediments
transported down any canyon system may be involved in erosional
downcutting, nonerosional bypass, deposition, or some combination of
these. Which occurs depends on eustacy, sediment supply, basin
subsidence, and tectonic controls. For the case of deposition within the
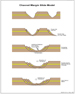
Rio Doce Canyon, we used a depositional model for infilling a sand-prone
canyon system modified from Cainelli (1992). Essentially, turbidity
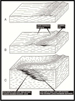
A second modern canyon system (oriented northwest-southeast) has no associated river to feed in sediment; sediment supply must come from a different, mostly non-shelf derived source. The model we applied to this system is modified from Shipp (1999) (Figure 4). The model invokes a series of faults parallel to the canyon walls that allow slumping onto the canyon center. This produces an uplift of sediment in the canyon center where slump blocks collide. The small uplift produced is above the baseline of equilibrium in the axis of the canyon. It will be eroded by any turbidite flow or the release of any buildup of water on the shelf caused by winds or storms. A model of this type will allow for the canyon system to grow larger (by headward erosion) but it will be for the most part a mud-dominated system. Sands that do exist within this system are still exploration targets, but the reserves are usually too small for deep-water economics. Since evaporite deposition in the Aptian, patterns of sediment transport into the Espirito Santo Basin have constantly evolved. Initially, low to moderate amounts of sediment were fed into the basin from the west. Later in the Cretaceous there was a reorganization of the coastal drainage patterns to the south in and around the Serra do Mar and the Serra da Mantiqueira coastal ranges (Campos Basin). This reorganization continued through the Eocene, directing sediment northward, eventually increasing the sediment supply into the Espirito Santo Basin (Bruhn, 1993). The uplift of these coastal ranges may also have trapped the ancient Rio Doce River into a specific canyon system. With the north-south trending salt ridges already in place offshore, the direction of sediment transport would also be north-south, parallel to the salt ridges (Figure 5).
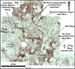
ConclusionsDominant controls on the stratigraphic evolution of the Espirito Santo Basin were: 1) Onset in Albian of autochthonous salt deformation; 2) Uplift of the Serra do Mar and Serra da Mantiqueira and a reorganization of the coastal drainage patterns starting in the Late Cretaceous; 3) Entrapment of the Rio Doce canyon system in the Eocene, delivering coarse-grained sediments into the deep-water. In the Eocene and younger section of the Espirito Santo Basin, high amplitudes within the canyons probably indicate coarse-grained sediment. Mapping the abrupt lateral changes in amplitude intensity and continuity is the easiest way to track the canyons through the basin. A time slice one second below the water-bottom (Figure 5) shows the sand-rich canyon systems as well as some sandy canyon systems. To identify
deeper buried Cretaceous canyons, an
ReferencesBruhn, C.H.L., 1993, High-resolution stratigraphy, reservoir geometry, and facies characterization of Cretaceous and Tertiary turbidites from Brazilian passive margin basins: Ph.D. Thesis, McMaster University, Canada, 433p. Cainelli, C., 1992, Sequence stratigraphy, canyons, and gravity mass-flow deposits in the Piacabucu Formation, Sergipe-Alagos Basin, Brazil: Ph.D Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin, 233p. Dauzacker, M.V., 1981, Basin analysis of evaporitic and post-evaporitic dDepositional systems, Espirito Santo Basin, Brazil, South America: Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin, 200p. Figueiredo, A.M.F., and Mohriak, W.U., 1984, A tectonica salifera e as acumulacoes de Petroleo da Bacia de Campos, in Proceedings of the 33rd Brazilian Geological Congress, Sociedada Brasileira de Geologia, Rio de Janeiro, v. 3, p. 1380-1394. Pereira, M.J., Barbosa, C.M., Agra, J., Gomes, J.B., Saito, M., Ramos, M.A., Carvalho, M.D., and Bagni, O., 1986, Estratigrafia da Bacia de Santos: Analise das sequencias, sistemas deposicionais e Revisao Litoestratigrafica, in Proceedings of the 34th Brazilian Geological Congress, Sociedade Brasileira de Geologia, Goiania, Brazil, v. 1, p. 65-79. Peres, W.E., 1990, Seismic-stratigraphic study of the Oligocene-Miocene shelf-fed turbidite systems of the Campos Basin, Brazil: Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin, 188p. Shipp, R.C., Shoup, R.C., and Diegel F.A., 1999, High–resolution near-surface analogs for deep subsurface canyon/channel-margin slides (Abstract). AAPG Bulletin, v. 83, p. 451
AcknowledgmentsThe authors would like to thank CGG Americas for permission to use the seismic data in this study. |