Seismic Modeling of Poroelasticity Using Asymptotic Formula of  Biot
Biot
Yangjun Liu
Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences University of Houston
Boits poroelasticity theory (1956) predicts movements of the pore fluid
relative to the skeleton as seismic waves propagate through the reservoir.
This phenomenon opens an opportunity for investigation of the permeability
of the hydrocarbon-saturated reservoirs from seismic amplitude. According
to  Biot
Biot , a compressional P-
, a compressional P- wave
wave in a fluid-saturated porous medium is a
superposition of fast and
in a fluid-saturated porous medium is a
superposition of fast and  slow
slow waves. The fast
waves. The fast  wave
wave is the classic P-
is the classic P- wave
wave ,
and the
,
and the  slow
slow
 wave
wave is a process of fluid-pressure diffusion.
is a process of fluid-pressure diffusion.
According to the asymptotic approximation of  Biot's
Biot's equation (Goloshu-
bin and Silin, 2006), the reflection coefficient for the fast normal incident
equation (Goloshu-
bin and Silin, 2006), the reflection coefficient for the fast normal incident
 wave
wave can be written in the following form:
can be written in the following form:
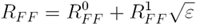
where R0FF and R1FF are the zero and first order expansion coefficients with respect to the dimensionless parameter
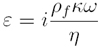
and, pf is the fluid density, k is the permeability of rock,
η is the fluid
viscosity, w is angular frequency, and 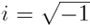 .
.
By using the above formula, a thin layer of porous media with porosity Φ=0,3 filled by water and gas alternatively is modeled by using the convolution method. The synthetic seismogram obtained shows a significant difference with the one obtained using the formula for elastic media. The permeability of the rock and seismic frequency also affect the seismic amplitude, such relationships are presented in this poster.
AAPG Search and Discover Article #90087 © 2008 AAPG/SEG Student Expo, Houston, Texas
